- Research Services
- Capabilities
- About Us
- Resources
- Contact Us
 Cecal Cannulation in Rats and Mice
Cecal Cannulation in Rats and Mice UUO in Mice and Rats
UUO in Mice and Rats Subcutaneous Minipump Placement
Subcutaneous Minipump Placement ACL Transection
ACL Transection Custom Surgical Models
Custom Surgical Models Surgery
SurgeryPrecise surgical techniques are often required for the induction of a specific disease model, collection of samples during the study, or for delivery of the test treatment to specific anatomical locations. BioModels offers a selection of established surgical models and techniques to support your preclinical program. Contact us for more information about an established surgical approach or to discuss a custom model or technique that supports your study goals.
BioModels offers a fully equipped facility to support:
The downstream effects of a novel treatment on disease progression and on the colonic tissue itself can be of great interest when testing drug candidates for treatment of intestinal diseases such as IBD. At BioModels, a cannula can be surgically placed into the cecum of mice and rats to allow for direct delivery of test material to the colon. The surgically placed cannula is stable for weeks, supporting longer term in-life studies such as the naïve TH cell adoptive transfer model. For more information on the surgical process and potential study design, email us to discuss further with one of our scientific team members.
Experimental Unilateral Ureter Obstruction (UUO) represents a model for obstructive nephropathy that is accomplished by surgically ligating the ureter below the left kidney. This model allows insight into the development of interstitial fibrosis which is a common characteristic of many chronic nephropathies. Important markers of renal fibrosis, such as interstitial fibroblasts, interstitial volume, mRNA and protein expression for collagen I, are all increased in UUO animals, making the UUO model a good experimental system for studying fibrosis. At BioModels, disease is induced when UUO is performed by ligating the ureter below the left kidney of a mouse on Day 0. In order to assess the development of disease, the kidneys are removed (for histological assessment of fibrosis) and blood is collected between day 7 and 14.
BioModels has the capability of systemic delivery of test articles or disease induction agent by use of an implanted subcutaneous minipump. Osmotic minipumps are available in a variety of sizes/volumes and can administer the agent of interest over different lengths of time depending on the needs of the study.
BioModels offers a model of surgically induced osteoarthritis (OA) in rats that can be used to test potential therapies for improving joint pain and preventing subsequent joint deterioration. Disease is induced by surgically transecting the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) without damaging the meniscus. The animals are allowed to move freely, and inflammation causes damage to the joint over time. OA is typically apparent beginning 4-5 weeks after induction. Though the rat OA model (unilateral ACL transection) relates to sports injuries in humans that can occur where the ACL is damaged or severed, the underlying disease processes are common to all joints affected by OA.
Specialized surgical techniques are sometimes required for the induction of a specific disease model, collection of samples during the in-life study, or for delivery of the test treatment to specific anatomical locations. In addition to established surgical models, BioModels also offers custom surgical techniques to support wound healing models, mesenteric lymph duct cannulation, orthotopic tumor models, and more. Reach out to our scientific team at info@biomodels.com to discuss adapting an established surgical model or for assistance in developing a custom model to support your project goals.
Capabilities


Close
Capabilities

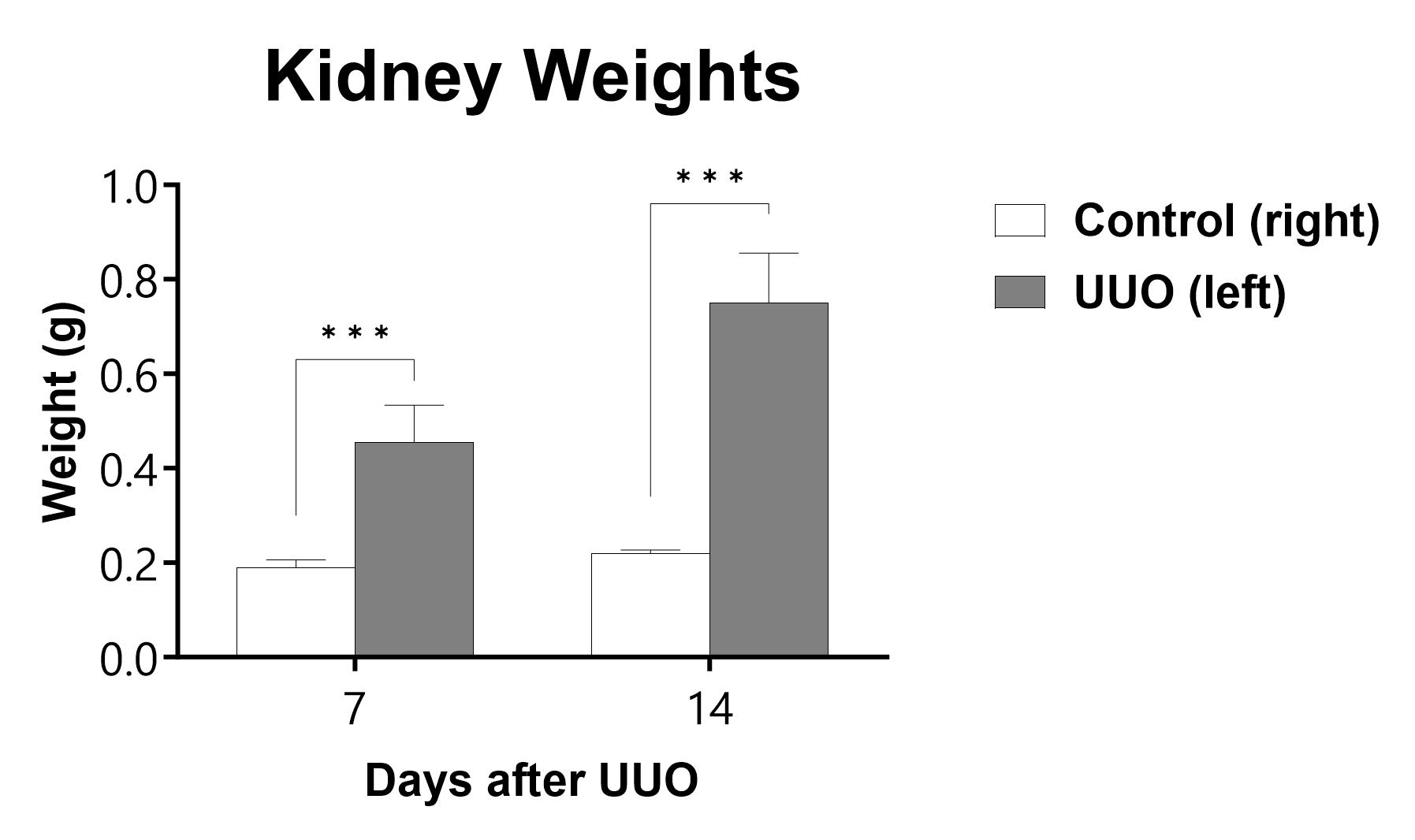
The UUO procedure is performed on C57Bl/6 mice on Day 0 and kidneys are collected and weighed at the specified endpoint. (***p<0.001 compared to the contralateral-control kidney)
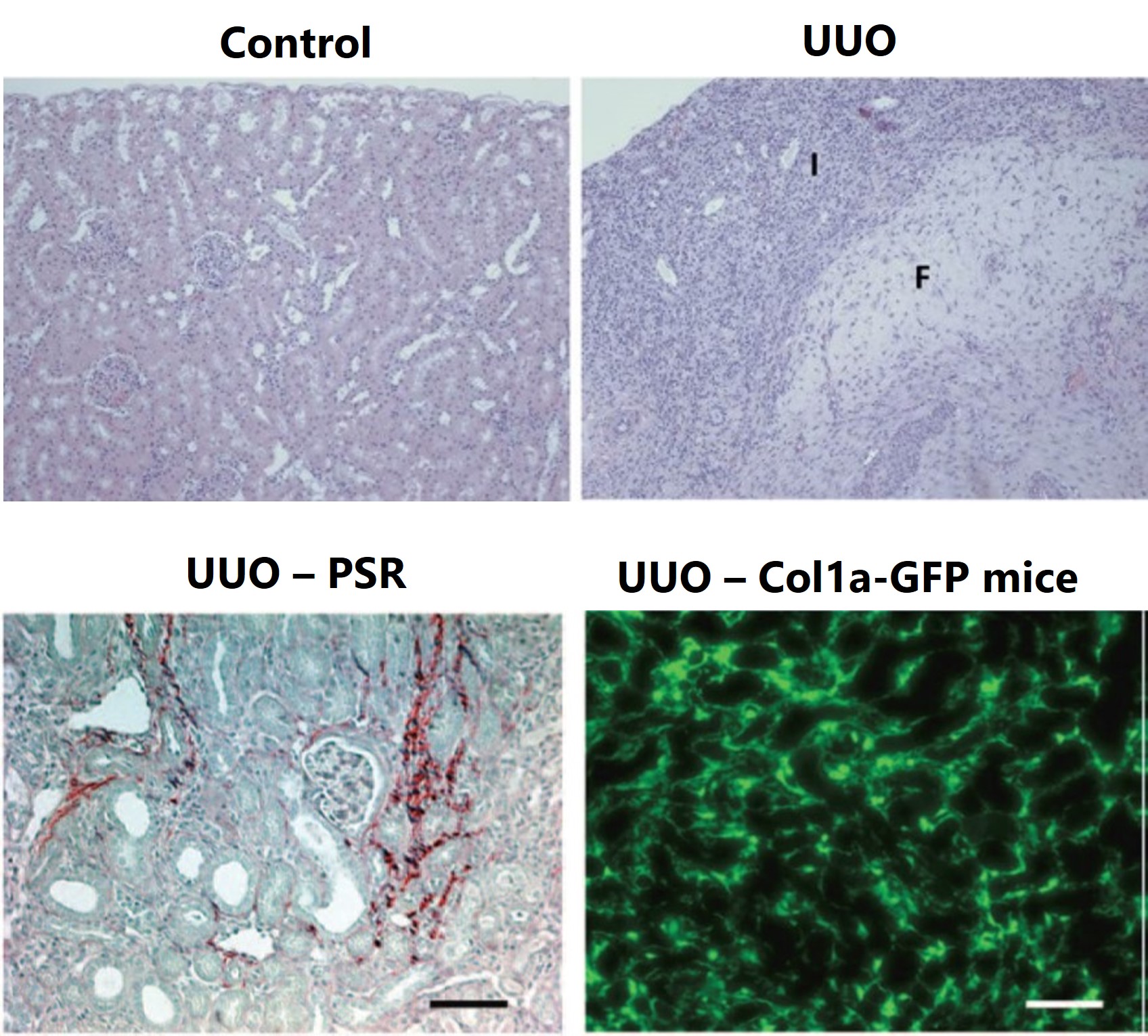
The UUO procedure is performed on C57Bl/6 mice on Day 0 and kidneys are collected for histopathology assessment in H&E-stained sections. Day 10 representative non-lesioned kidney cortex in control kidney and areas of inflammation (I) and fibrosis (F) in UUO kidney are displayed. Day 14 representative images of UUO kidney are shown with picrosirius red staining (bottom left). Day 14 representative images of UUO kidney from Col1a-GFP mice (bottom right).

Close
Capabilities

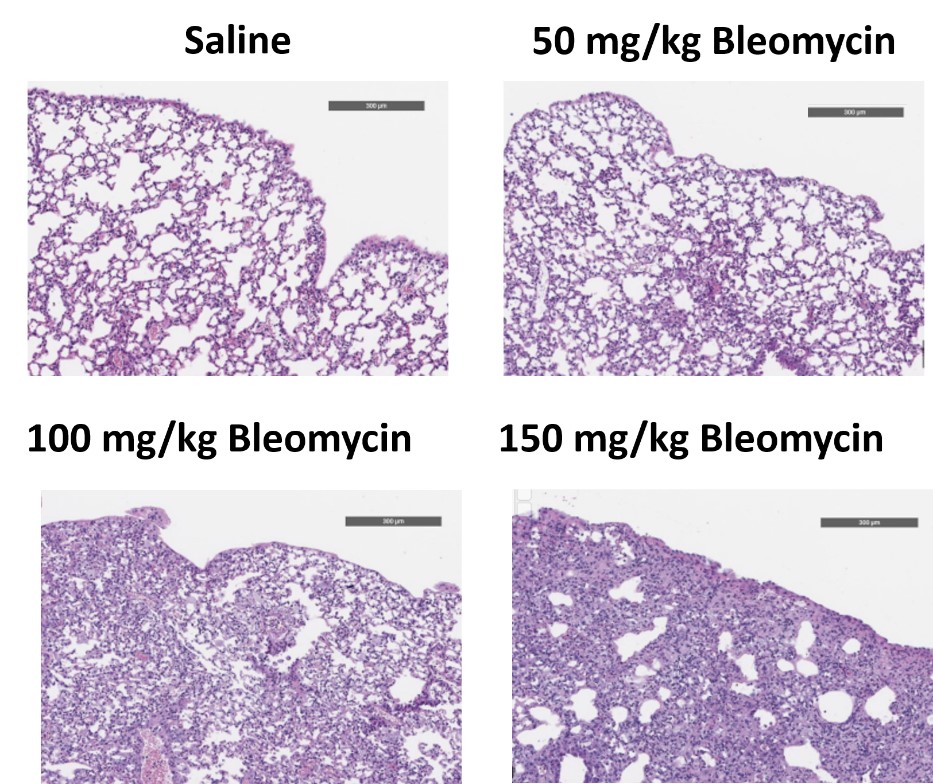
C57Bl/6 mice are administered Bleomycin for 28 days through a SC implanted osmotic pump and Day 28 lungs are processed for histopathology. H&E-stained lungs from animals administered saline or 50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, or 150 mg/kg Bleomycin.
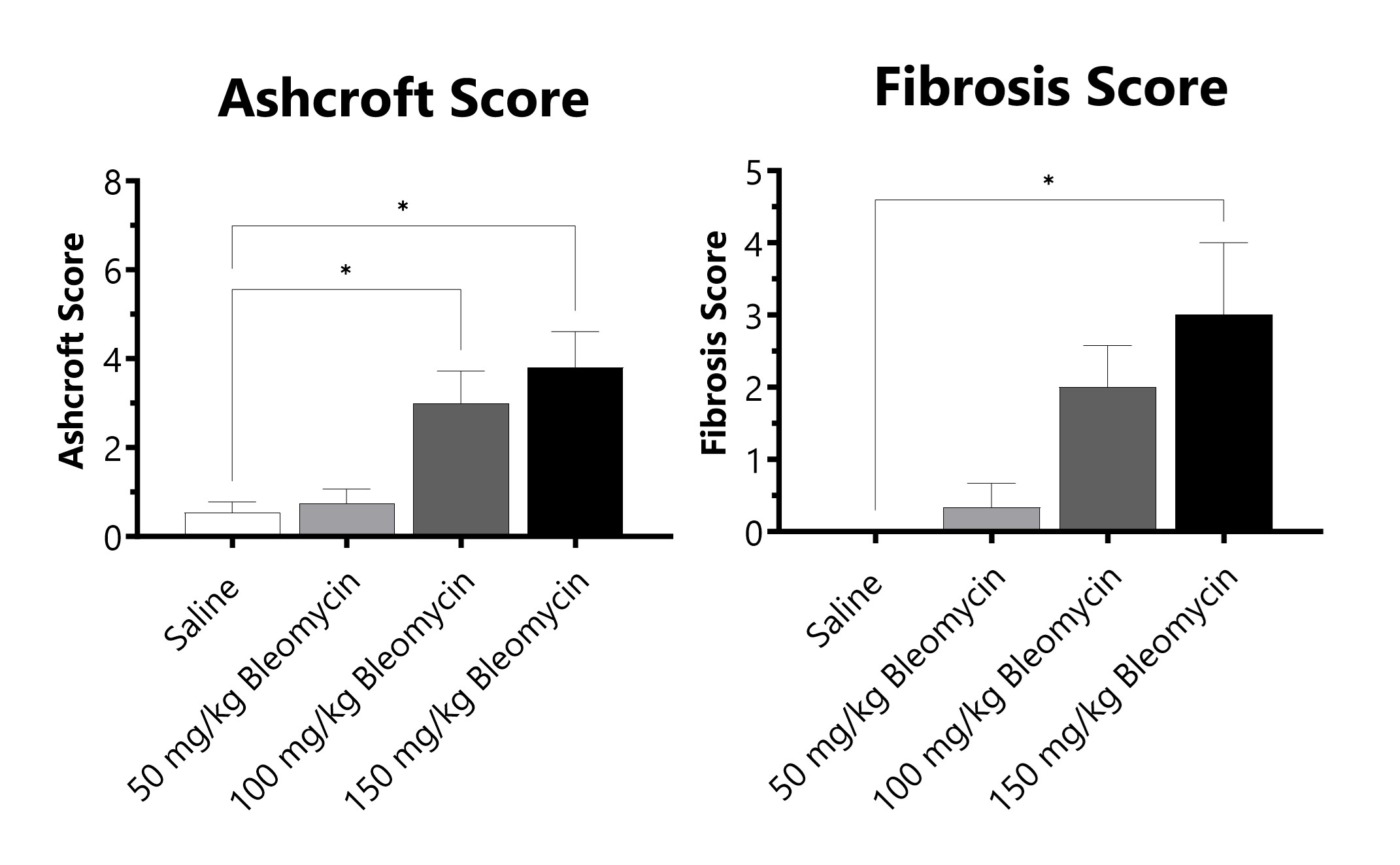
C57Bl/6 mice are administered Bleomycin for 28 days through a SC implanted osmotic pump. Pathology assessment of Day 28 lungs from SC Osmotic Pump-Bleomycin administered animals. Ashcroft score is determined in H&E-stained tissue using a modified Ashcroft Scale graded from 0-8. Fibrosis score is determined in Masson’s Trichrome-stained tissue using a 0-5 semi-quantitative scoring scale of area staining positive for collagen. (*p<0.05 compared to the saline-control).
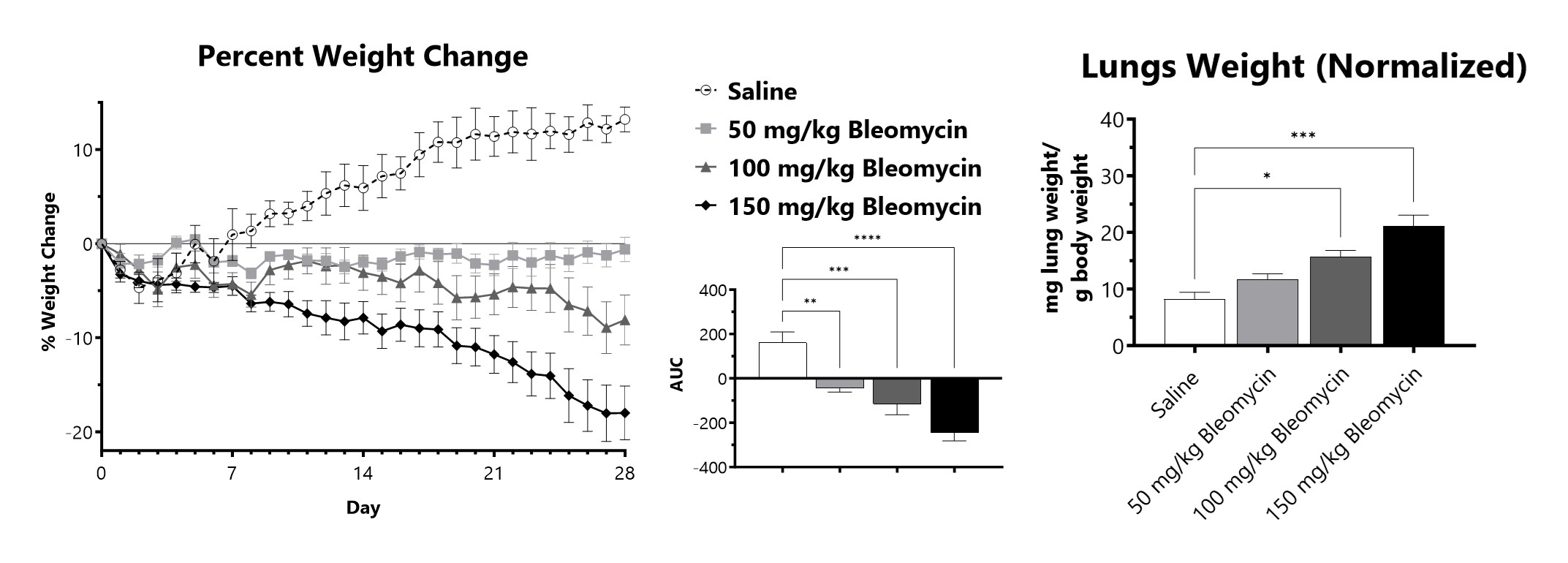
C57Bl/6 mice are administered Bleomycin for 28 days through a SC implanted osmotic pump. Animals are weighed daily, and body weight compared to Day 0 is calculated. The AUC is calculated to compare treatment arms and is shown in the inset. Wet lung weight normalized to Day 28 body weight of Day 28 lungs from SC Osmotic Pump-Bleomycin administered animals. (*p<0.05; ***p<0.001 compared to the saline-control)
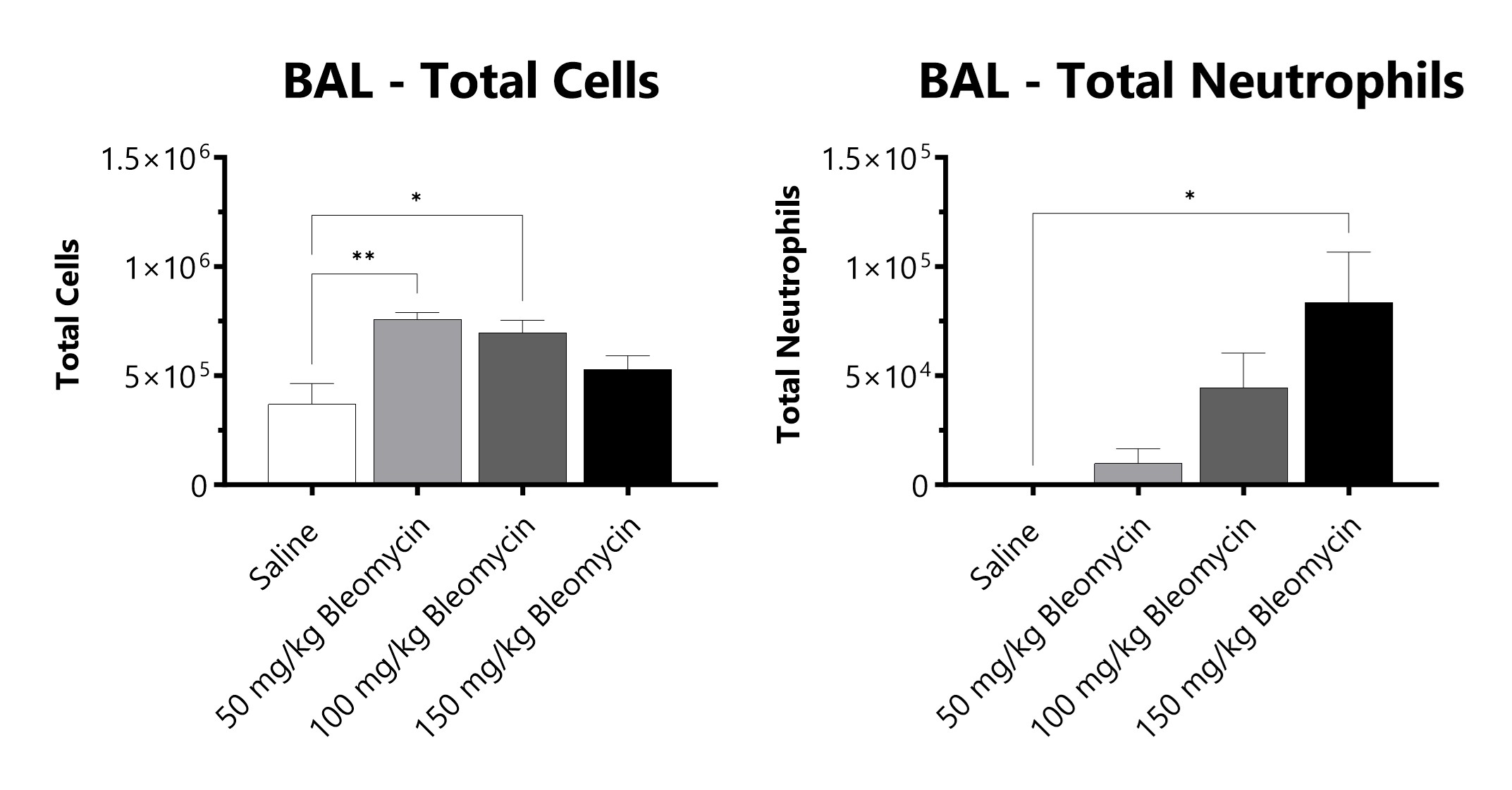
C57Bl/6 mice are administered Bleomycin for 28 days through a SC implanted osmotic pump and BAL fluid is assessed at 28 days for total cells and total neutrophils following administration of either 50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, or 150 mg/kg Bleomycin. (*p<0.05; **p<0.01 compared to the saline-control).
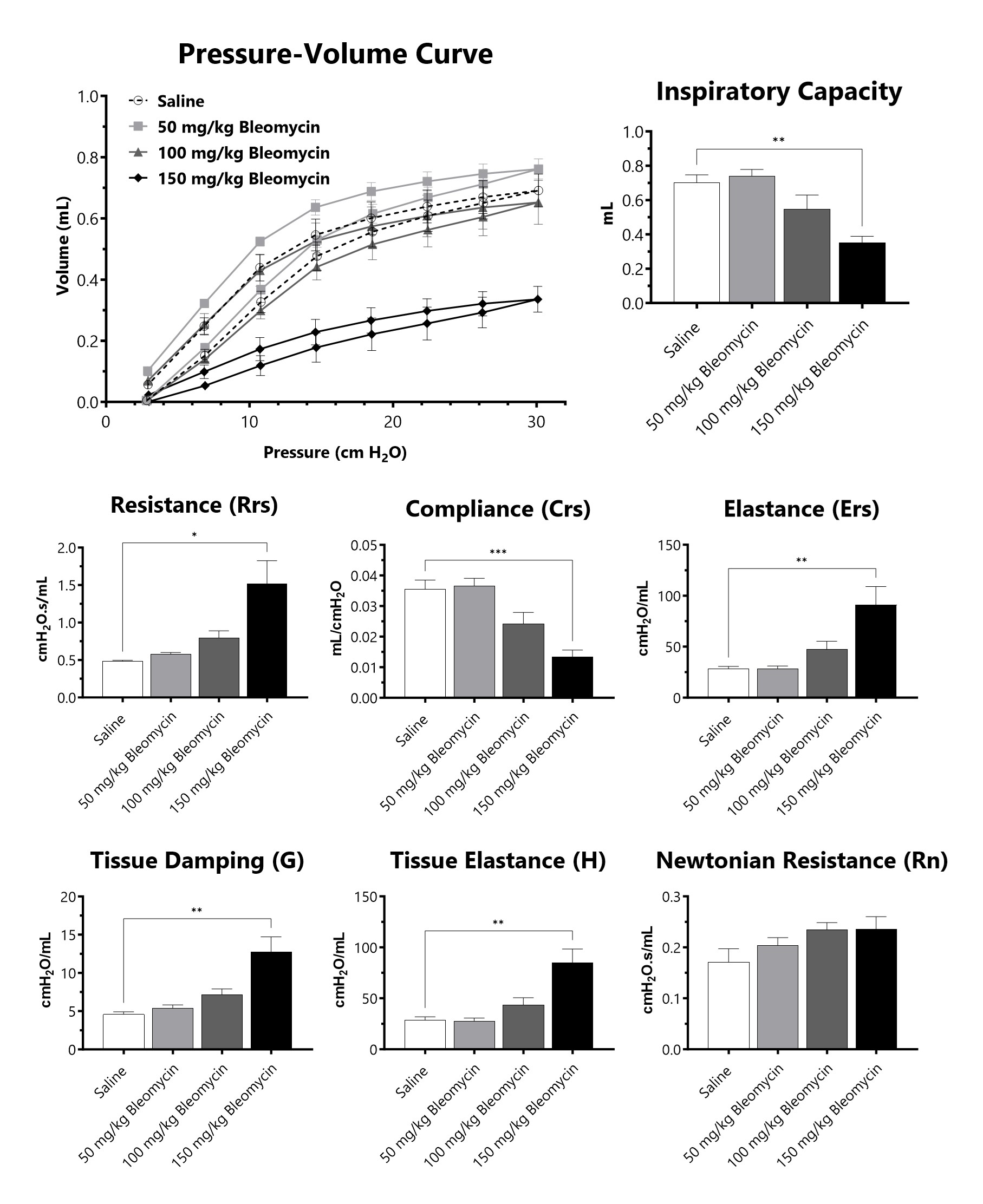
C57Bl/6 mice are administered Bleomycin for 28 days through a SC implanted osmotic pump and lung mechanics are assessed at 28 days following administration of either 50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, or 150 mg/kg Bleomycin. (*p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001 compared to the saline-control).
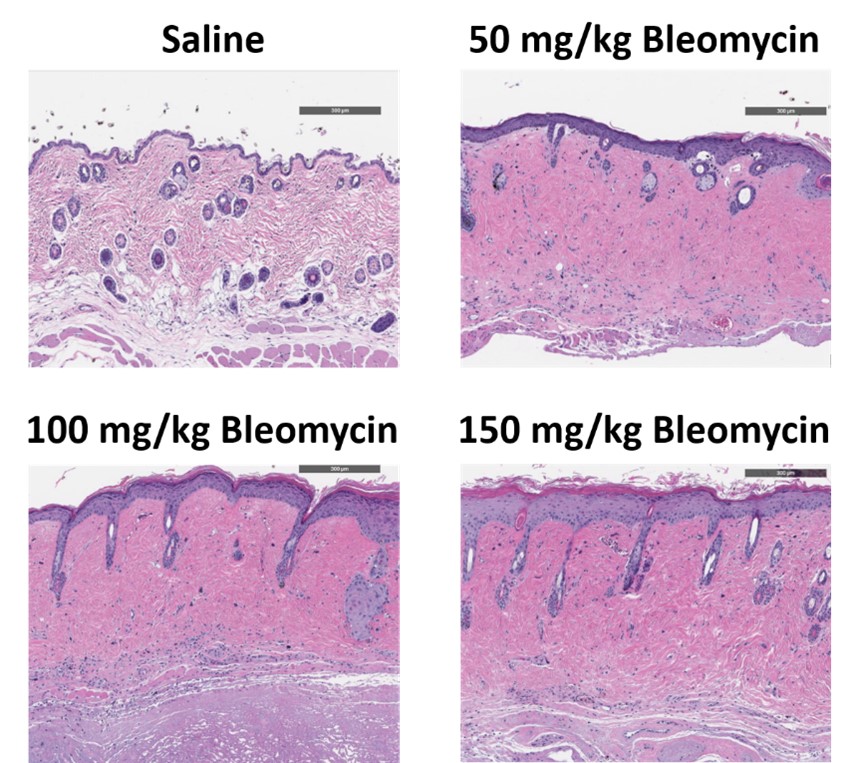
C57Bl/6 mice are administered Bleomycin for 28 days through a SC implanted osmotic pump and Day 28 skin samples are processed for histopathology. H&E-stained skin from animals administered saline or 50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, or 150 mg/kg Bleomycin.
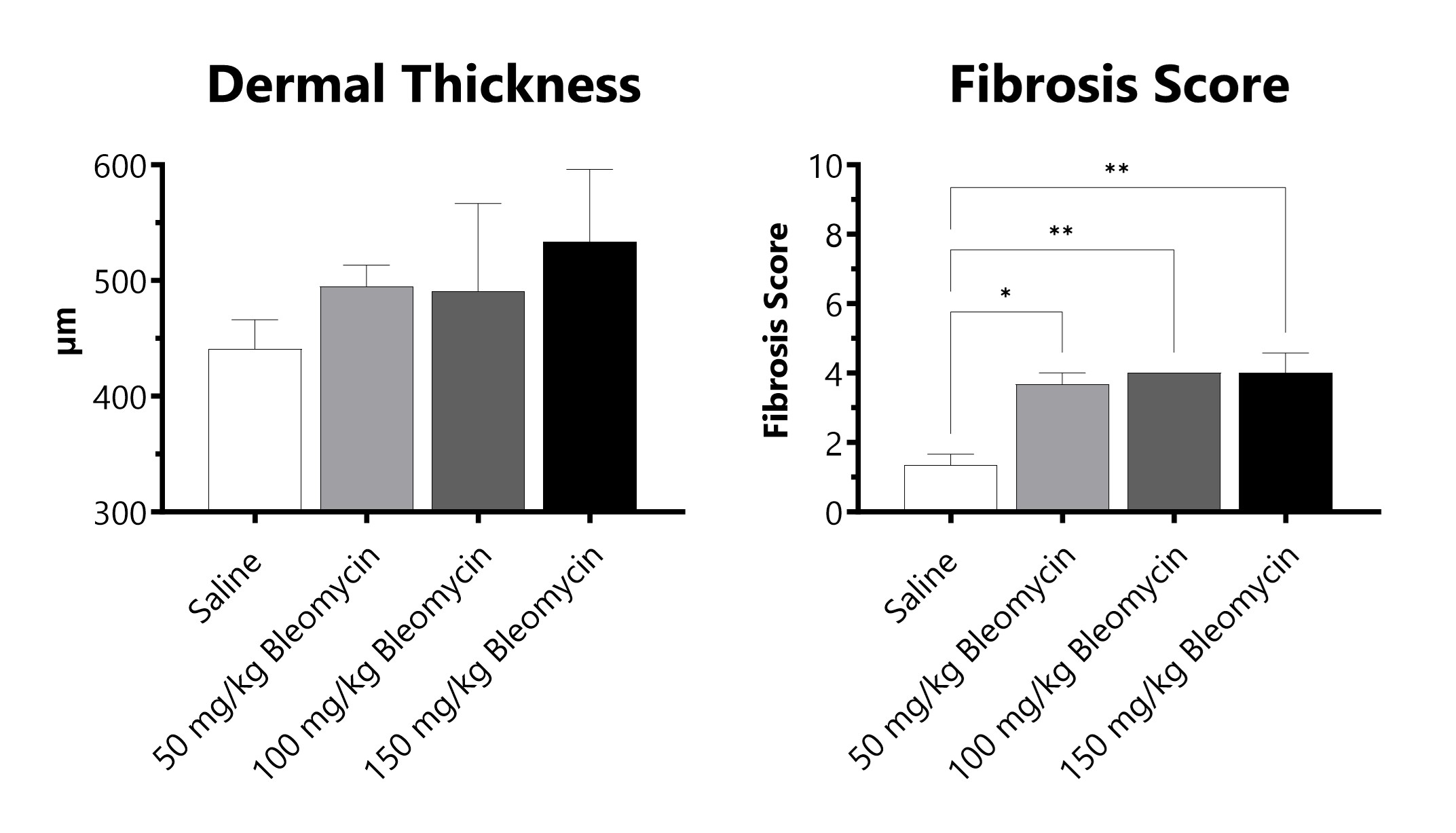
C57Bl/6 mice are administered Bleomycin for 28 days through a SC implanted osmotic pump. Pathology assessment of Day 28 skin from SC Osmotic Pump-Bleomycin administered animals. Dermal thickness is measured, and fibrosis score is determined in Masson’s Trichrome-stained tissue using a 0-5 semi-quantitative scoring scale of area staining positive for collagen. (*p<0.05; **p<0.01 compared to the saline-control)

Close
Capabilities

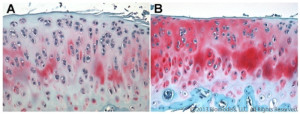
Representative Safranin O stained rat articular cartilage 36 days following ACL transection. (A) PBS-treated, (B) Treated with intra-articular Enbrel injections that began 7 days after surgery and occurred twice weekly. Histopathology performed by Dallas Tissue Research.
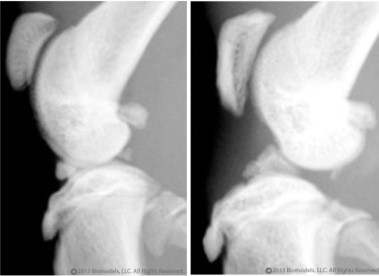
Lateral radiograph on left is from a normal rat, lateral radiograph on right is from a rat 32 days after of ACL transection.

Close