- Research Services
- Capabilities
- About Us
- Resources
- Contact Us
 Oral Mucositis
Oral Mucositis Radiation-Induced Dermatitis
Radiation-Induced Dermatitis Proctitis
Proctitis Additional Cancer Supportive Care Diseases Models
Additional Cancer Supportive Care Diseases Models Cancer Supportive Care
Cancer Supportive CareBioModels is internationally recognized for its groundbreaking work in oral mucositis. Additional models have also been developed to address unmet needs for the toxicities associated with treatment of diverse cancers. With the dramatic improvement in the survivorship of cancer patients, increased resources have been applied to the development of new drugs and therapeutics for the complications associated with cancer treatment.
Work with BioModels to:
At BioModels, you can assess your novel therapeutics for efficacy and mechanism of action in our industry-leading, highly translatable oral mucositis models that address unmet needs in the cancer supportive care space. Oral ulcerative mucositis is a common, painful, dose-limiting toxicity of drug and radiation therapy that occurs during the treatment of cancer. Select the best model, acute or fractionated, based on your potential targets and study goals.
Our literature-validated experimental endpoints include:
Assess your novel therapeutics for efficacy and mechanism of action in our established dermatitis models to address unmet clinical needs for patients undergoing radiation therapy. Dermatitis is an umbrella term for a group of conditions that cause inflammation of the skin and is one of the most common side effects of radiotherapy for certain cancers. We offer both acute and fractionated mouse models of radiation induced dermatitis, which are well-established in the literature and provide clinically relevant disease phenotypes.
Our literature-validated experimental endpoints include:
Assess your novel therapeutics for efficacy and/or mechanism of action in our established models of radiation-induced proctitis. Radiotherapy is an important method of treatment for many pelvic and GI malignancies. However, with radiation in this region, it can result in the development of acute or even chronic proctitis that can severely impact the patient’s quality of life and ability to tolerate additional cancer treatment. Select the best model, acute or fractionated, based on your potential targets and study goals.
Our literature-validated experimental endpoints include:
At BioModels, you can assess your novel therapeutics for efficacy and/or mechanism of action in our various preclinical models that address unmet needs in the cancer supportive care space. BioModels is the world leader in Cancer Supportive Care research through its expertise in developing innovative models based on a thorough understanding of the toxicities associated with chemotherapy and radiotherapy in the treatment of carcinomas. Work with the BioModels team to select the best model for your research goals.
Some of our literature-validated experimental endpoints include:
Study Models

Mucositis occurs to some degree in more than one third of patients receiving anti-neoplastic drug therapy, resulting in lower quality of life, a reduction in adherence to the treatment schedule, and potentially more serious complications such as bacteremia. In the acute radiation-induced oral mucositis model at BioModels, a bolus x-ray radiation dose is delivered to the cheek pouch of hamsters while the rest of the animal’s body is shielded. Hamsters provide an excellent model for oral mucositis because of several biological similarities to humans providing high predictive validity. Ulceration of the cheek pouch oral mucosa approximately 16-18 days after radiation. Primary endpoints in this model include clinical mucositis scoring using a validated scale and analysis of the frequency and duration of ulceration, mimicking the key endpoints in cancer patients. Radio-sensitizing chemotherapy can also be combined with radiation treatment.
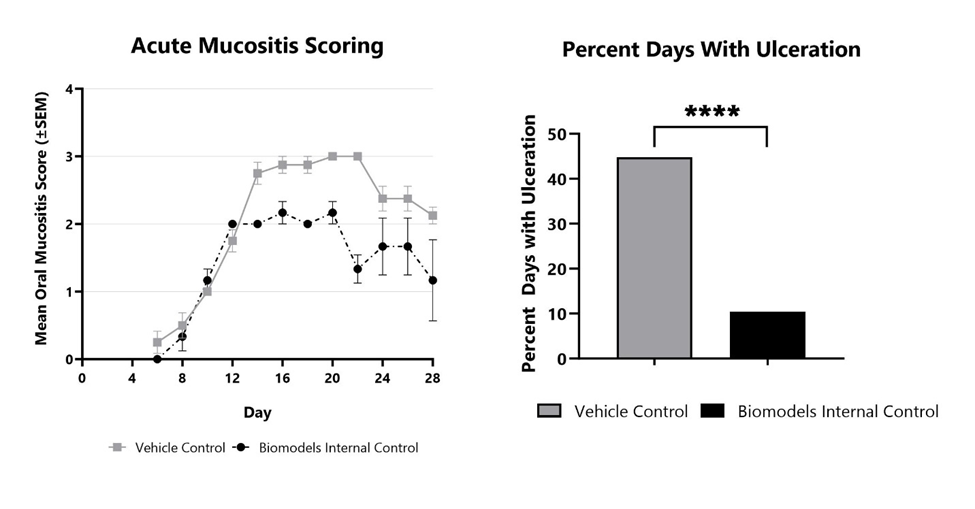
Acute oral mucositis is induced using a 40Gy bolus of x-ray radiation. The disease is evaluated every other day from Day 6 to the end of the study using a validated scoring scale. Vehicle control and Biomodels Internal Control are shown. Percent days with ulceration with each treatment are shown on the right. ****p<0.0001.

Close

In the fractionated radiation-induced oral mucositis model in hamsters, disease is induced with daily smaller doses of radiation (x-ray) directed at the cheek pouch while the remainder of the animal’s body is shielded. The fractionated model provides increased translatability as patients often undergo several weeks of daily radiation treatment. As with the acute model, primary endpoints include clinical mucositis scoring using a validated scale and analysis of the frequency and duration of ulceration, mimicking the key endpoints in cancer patients. Radio-sensitizing chemotherapy can also be combined with radiation treatment.
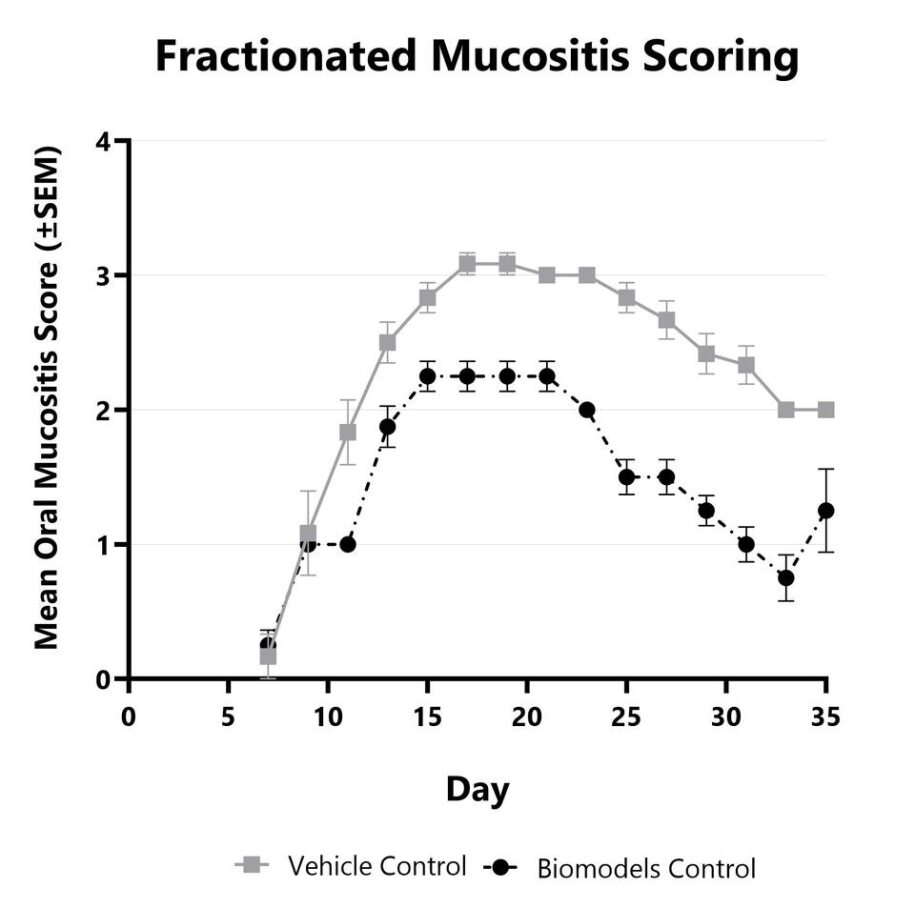
Fractionated oral mucositis is induced using eight 7.5Gy x-ray radiation doses. The disease is evaluated every other day from Day 7 to the end of the study using a validated scoring scale. Vehicle control and BioModels Internal Control are shown.

Close

In some experimental cases, it is advantageous to utilize more common laboratory animal species such as rats or mice due to the increased availability of regents or genetic variants. BioModels has developed an acute radiation model of oral mucositis in both mice and rats that results in ulceration of the oral mucosa that can be assessed via visual scoring that uses a validated scoring scale and/or histopathology. Contact BioModels to discuss the models in more detail and to customize the approach to meet your study goals.

Close
Study Models

Dermatitis is an inflammatory condition of the skin often occurring as a result of exposure to ionizing radiation during radiation therapy for a variety of malignancies. Chronic radiation-induced dermatitis occurs over a longer period of time and involves irreversible and progressive fibrosis. Ionizing radiation results in DNA damage leading to cell death in addition to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). At BioModels, acute radiation dermatitis is induced in mice using a single bolus of acute radiation (x-ray). Animals are monitored daily and evaluated for overall health and survival in addition to dermatitis severity over the course of the study. Peak disease typically occurs between Day 12 and Day 14, with disease persisting through the final evaluation which typically includes histopathology.
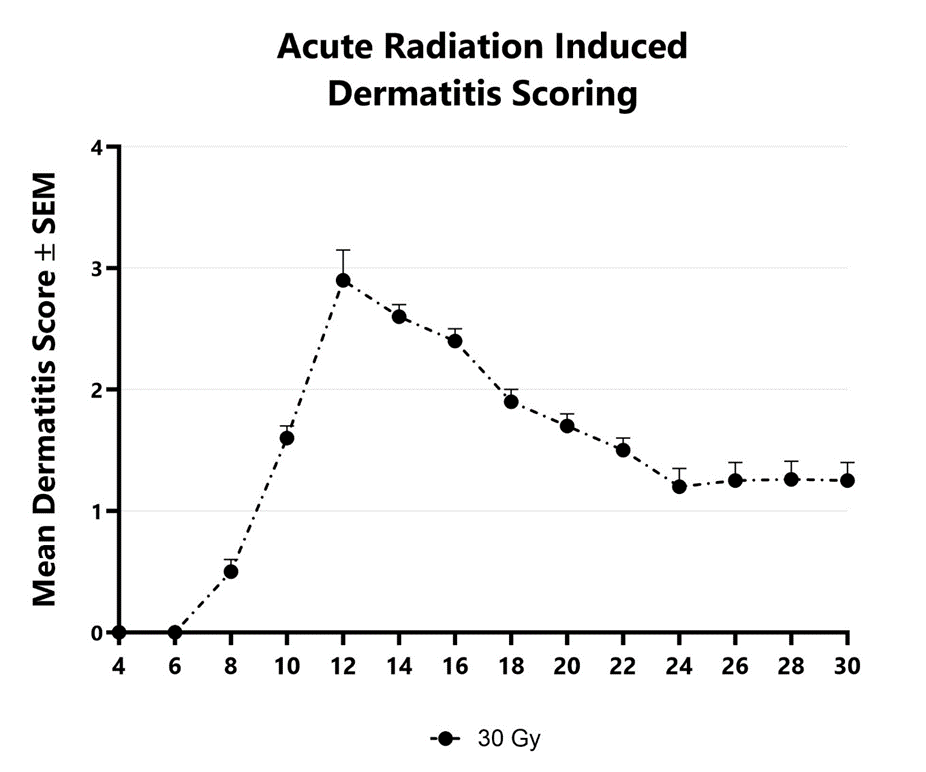
Dermatitis severity is assessed longitudinally using a pre-established scoring scale at multiple timepoints during an acute radiation-induced dermatitis study.

Close

In the fractionated radiation-induced dermatitis model at BioModels, disease is induced using 6 fractionated, smaller doses of targeted radiation to the skin of mice while the rest of the body is protected by a lead shield. Animals are monitored daily and evaluated for overall health and survival in addition to dermatitis severity over the course of the study. Peak disease typically occurs between Day 14 and Day 16, with disease persisting through the final evaluation which typically includes histopathology.
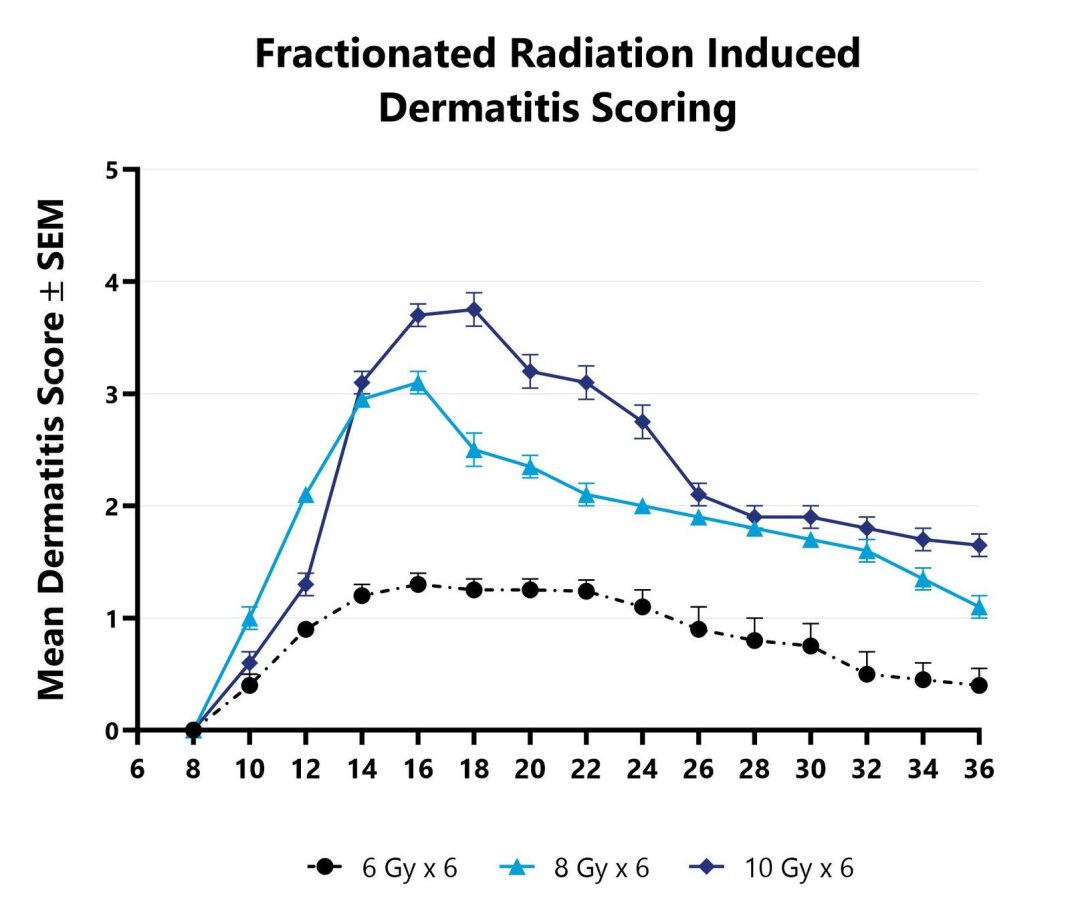
Dermatitis severity is assessed longitudinally using a pre-established scoring scale at multiple timepoints during an acute radiation-induced dermatitis study.

Close
Study Models

Radiation-induced proctitis is a common complication associated with radiation directed to the abdomen and/or pelvis in the treatment of rectal, prostate, or cervical malignancies. The direct effect of ionizing radiation during radiation therapy damages the DNA, lipids, and proteins of cells (both cancerous and non-cancerous) in the GI tract. In the acute radiation-induced proctitis model in rodents, disease is induced with a single bolus of radiation directed to the distal colon. Animals are monitored daily and evaluated for overall health and survival in addition to diarrhea and bloody stool incidence. A major readout in the model is proctitis severity determined via longitudinal video endoscopic assessments over the course of the study. Peak proctitis severity typically occurs around Day 7 or Day 8, with disease persisting through the final evaluation which often includes histopathology.
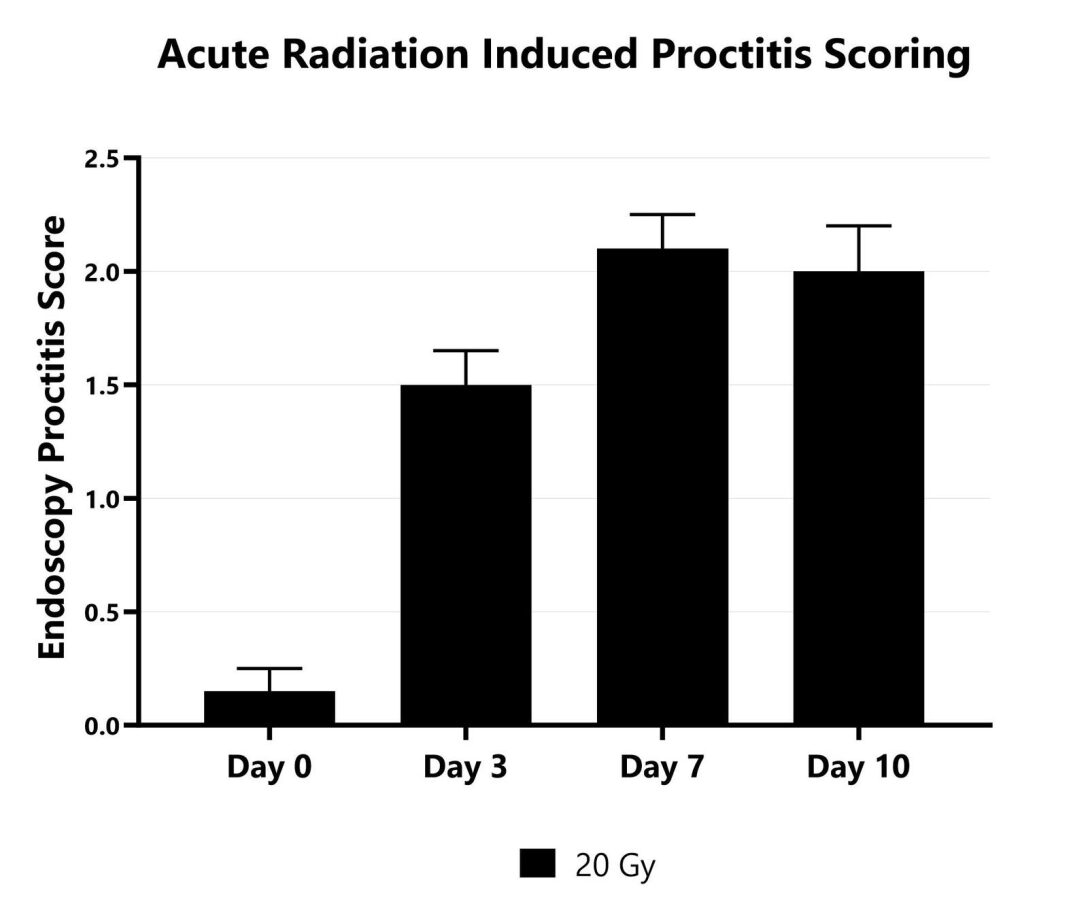
Proctitis severity is assessed longitudinally using video endoscopy at multiple timepoints during an acute radiation-induced proctitis study.
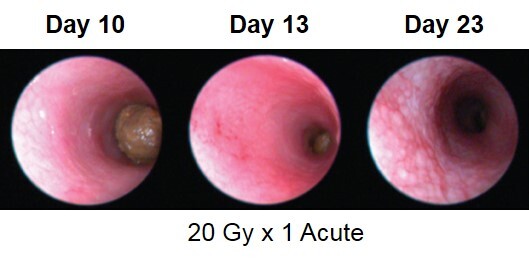
Proctitis severity is assessed longitudinally using video endoscopy at multiple timepoints during an acute radiation-induced proctitis study.

Close

In the fractionated radiation-induced proctitis model, disease is induced with several smaller doses of radiation directed to the distal colon. Animals are monitored daily and evaluated for overall health and survival in addition to diarrhea and bloody stool incidence. A major readout in the model is proctitis severity determined via longitudinal video endoscopic assessments over the course of the study. Peak disease in the fractionated model typically occurs around Day 13 to Day 14, with disease persisting through the final evaluation which often includes histopathology.
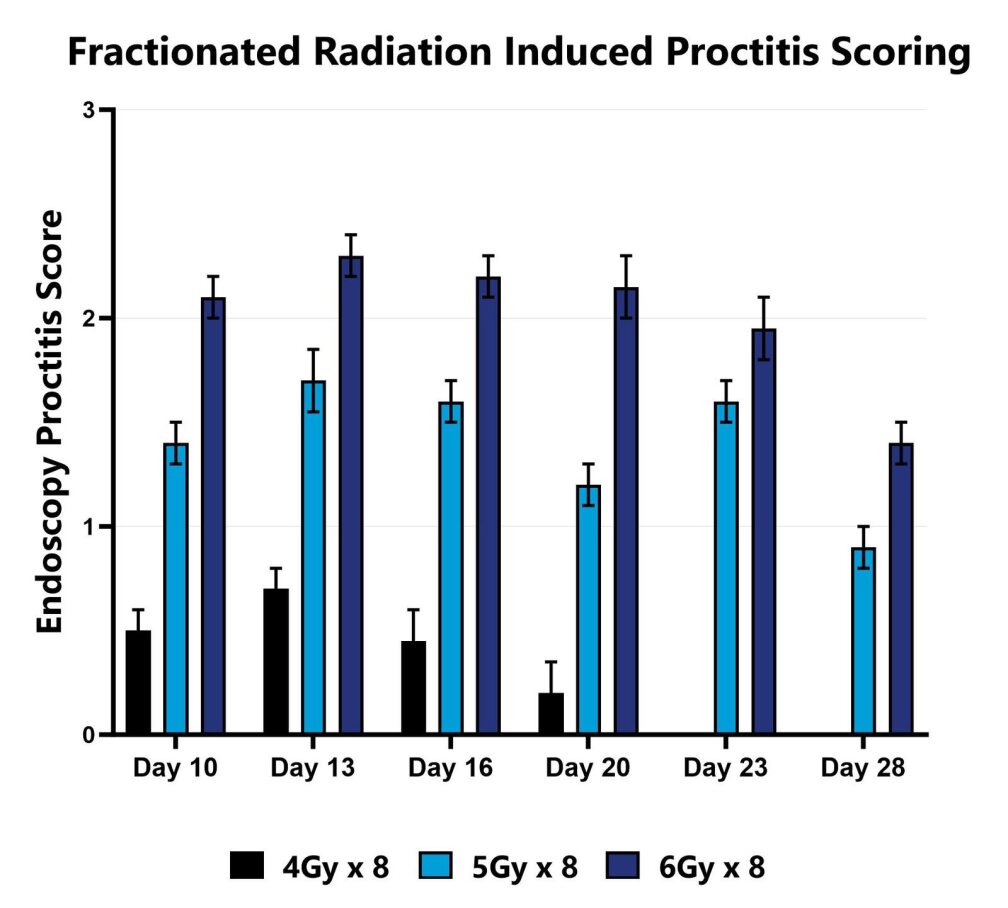
Proctitis severity is assessed longitudinally using video endoscopy at multiple timepoints during a fractionated radiation-induced proctitis study.
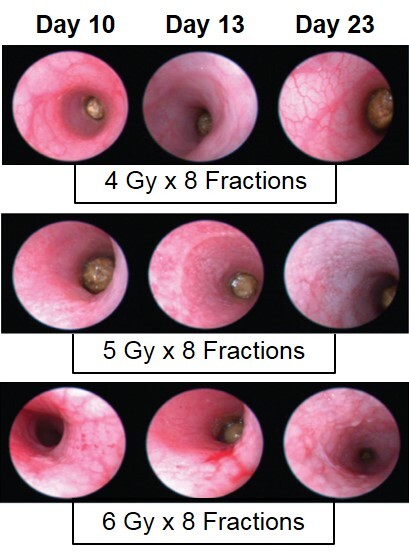
Proctitis severity is assessed longitudinally using video endoscopy at multiple timepoints during a fractionated radiation-induced proctitis study.

Close
Study Models

Fatigue related to cancer and cancer treatment is one of the most common symptoms reported by cancer patients. Fatigue negatively impacts quality of life and in some cases may even influence a patients’ decision to continue treatment. BioModels has developed an animal model of chemotherapy-related fatigue in which mice are treated with two cycles of doxorubicin followed by daily evaluation of wheel running activity. Chemotherapy treatment results in a significant reduction in voluntary wheel running activity, typically occurring in the second half of the wake cycle, mimicking patient-reported symptoms. There is currently an unmet need for effective therapies to treat fatigue. No pharmaceutical therapies are currently approved for fatigue.
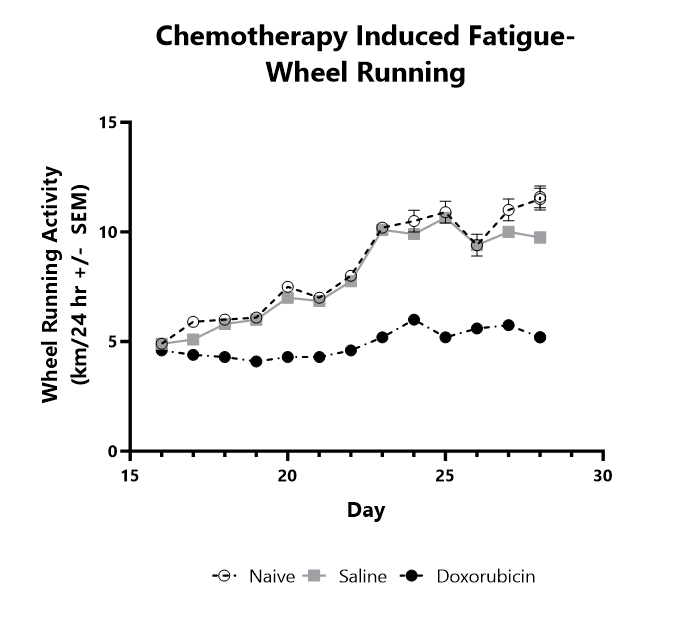
Mice are treated with two cycles of doxorubicin followed by daily evaluation of wheel running activity. Average wheel running activity is shown.

Close

At BioModels, you can assess your novel therapeutics for efficacy and mechanism of action in our established chemotherapy-induced diarrhea model to address unmet clinical needs for patients. Diarrhea is one of the most common toxicities associated with chemotherapy, reported in up to 80% of patients, leading to serious physical insufficiency, and disruption of treatment. BioModels’ chemotherapy-induced diarrhea model utilizes well validated dose concentrations and schedules of common chemotherapeutic agents to reproducibly induce diarrhea of known duration and severity in rats or mice. Animals are assessed daily over the course of the study for survival and weight change. Other important readouts include endoscopy, stool consistency scoring, food and water consumption, and terminal histopathology.
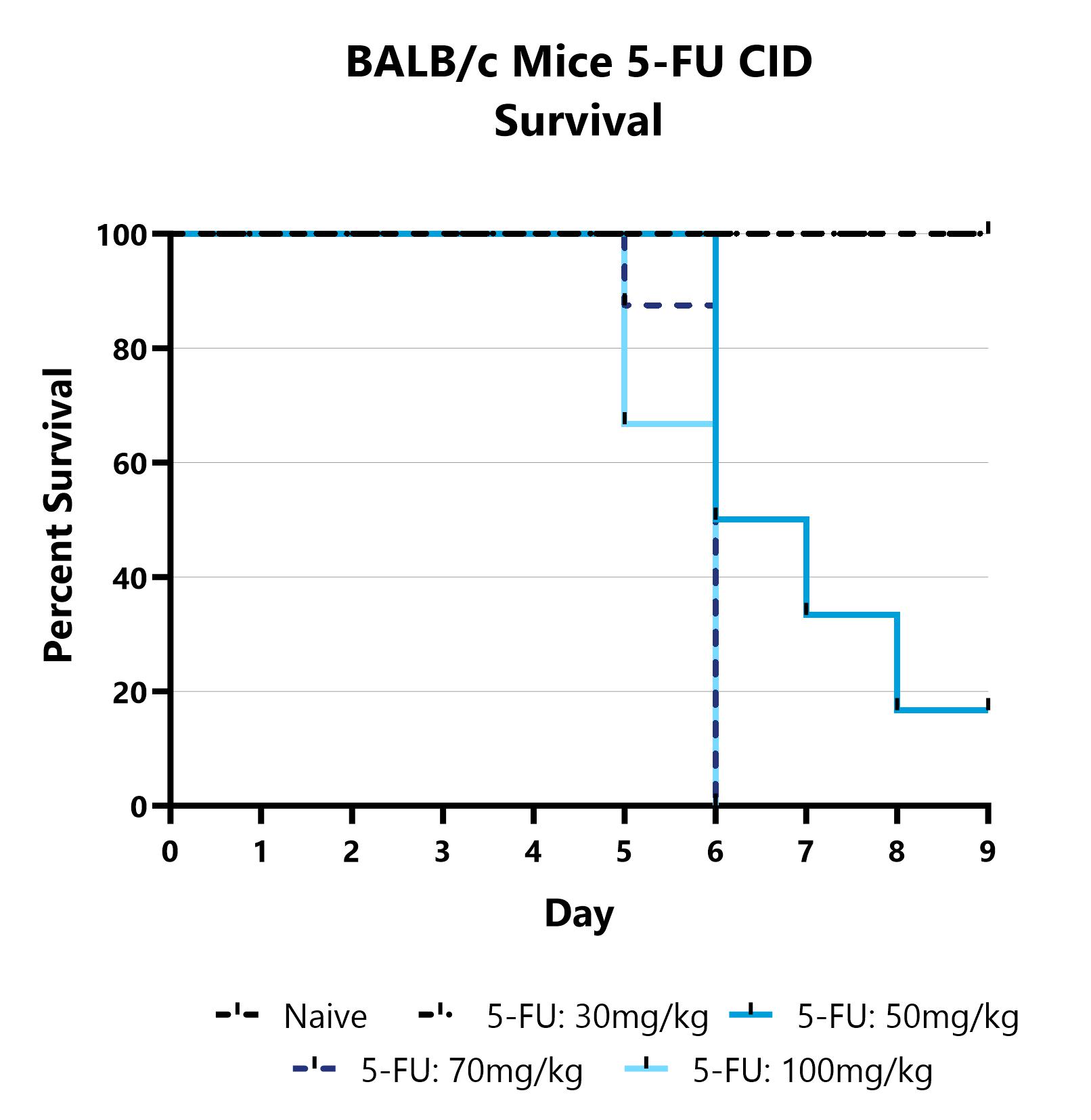
Mice are treated with 5-FU via IP injection on Days 0-4 and monitored daily for 9 days. Survival is evaluated daily and reported as the group mean for each day.
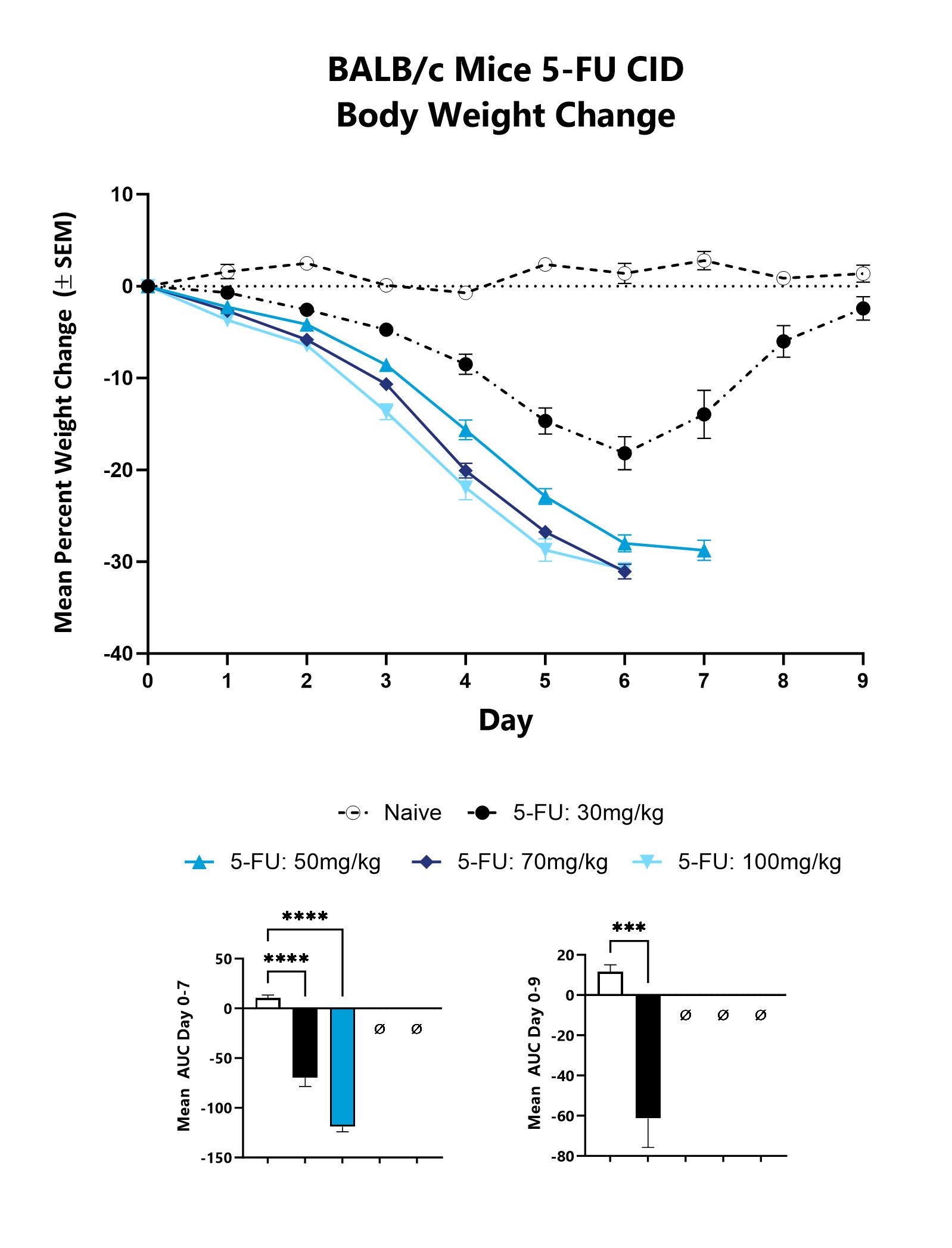
Animals are weighed daily, and body weight changes as compared to Day 0 are calculated. The AUC is calculated to compare treatment arms and is shown in lower graphs. (***p<0.001;****p<0.0001).
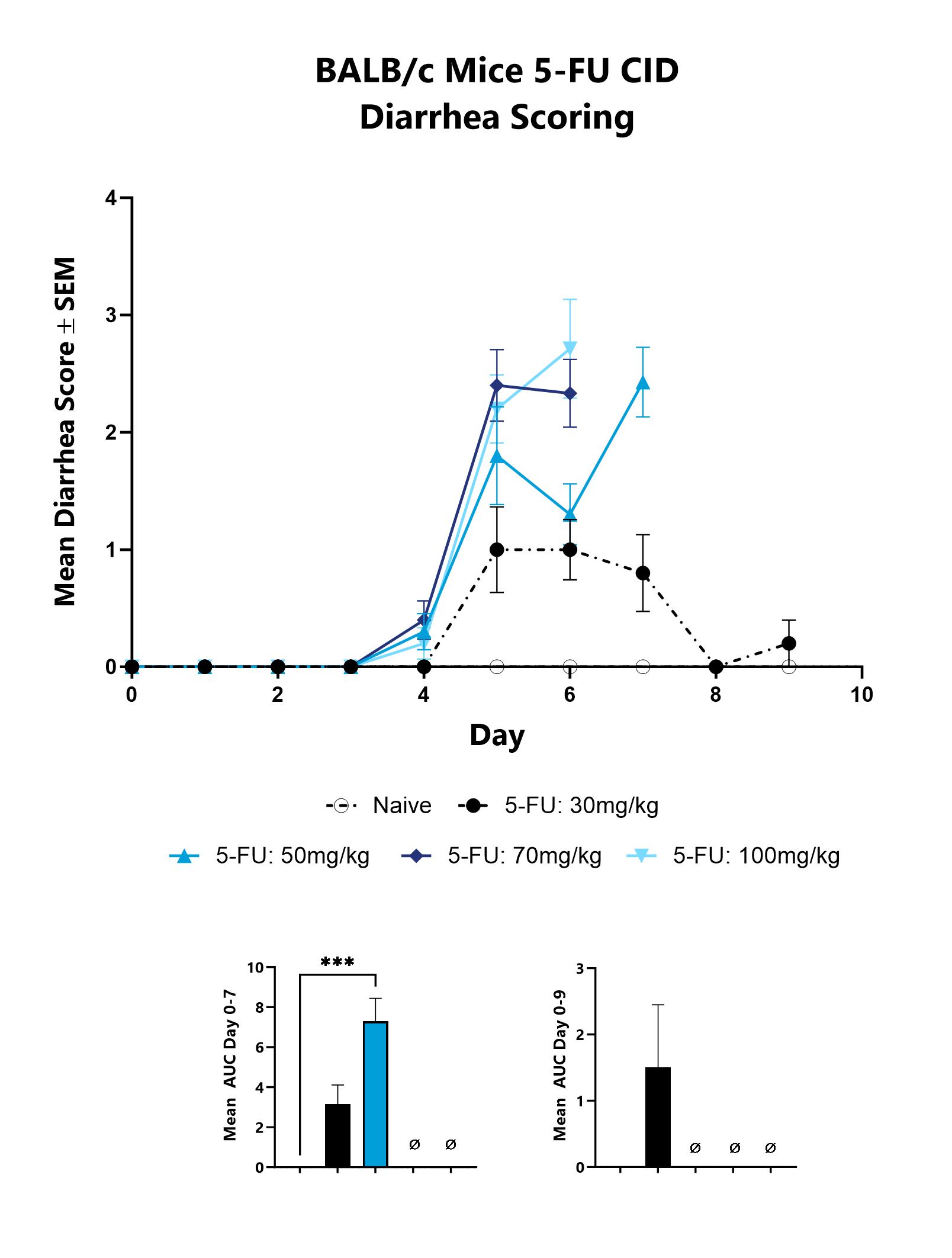
Mice with CID are assessed daily for diarrhea development. Each animal is assigned a score on a scale of 0-4, and the group mean is shown. The AUC is calculated to compare treatment arms and is shown in the inset. (***p<0.001).
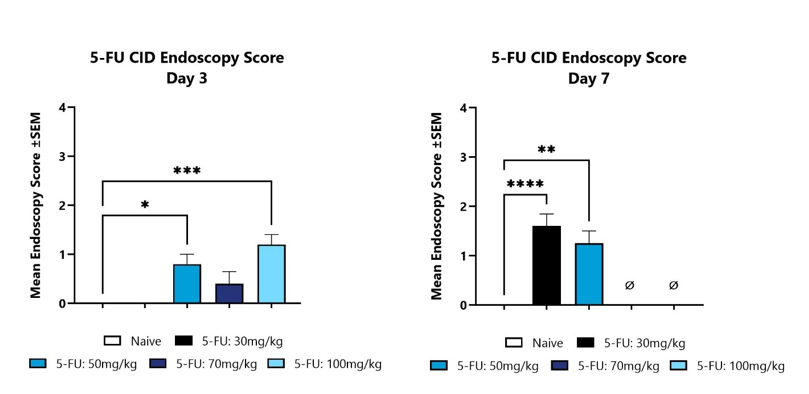
Animals with CID are assessed for colon inflammation by video endoscopy and are scored on a validated scale of 0-4. The mean group score is shown for Day 3 (left) and Day 7 (Right). (*p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001 compared to the Naïve control group).
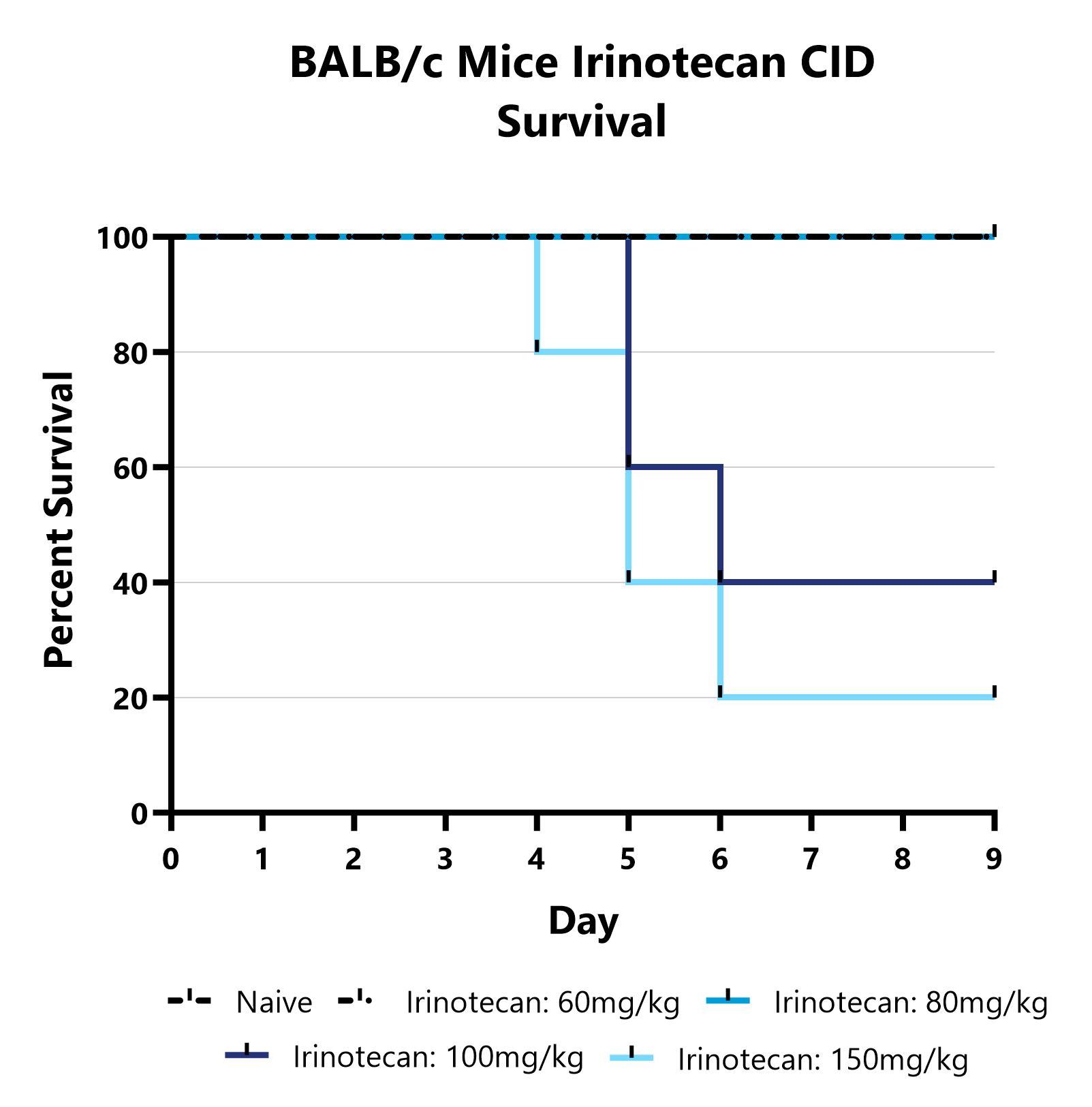
Mice are treated with Irinotecan via IP injection on Days 0-3 and monitored daily for 9 days. Survival is evaluated daily and reported as the group mean for each day.
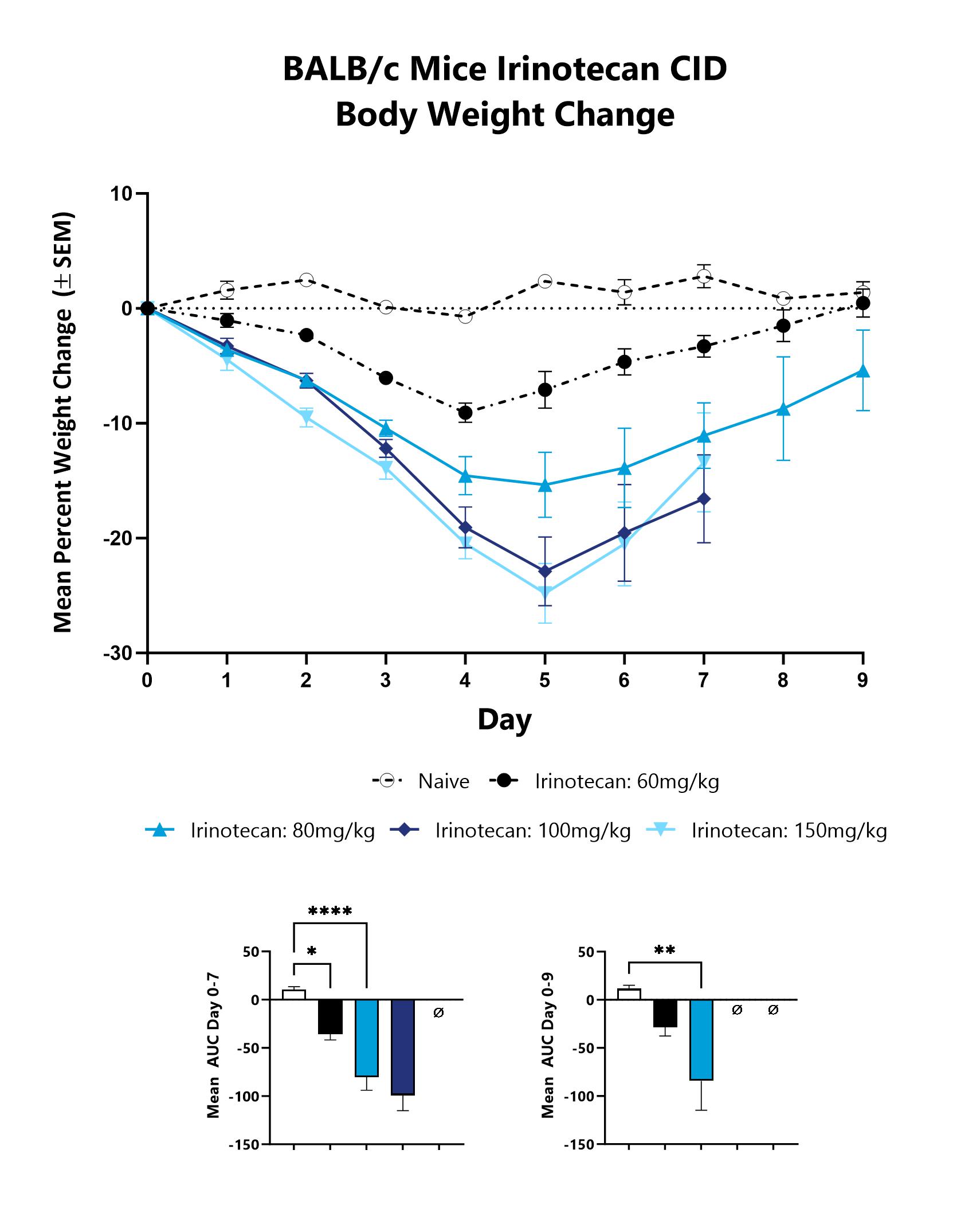
Animals are weighed daily, and body weight changes as compared to Day 0 are calculated. The AUC is calculated to compare treatment arms and is shown in lower graphs. (*p<0.05;**p<0.01;****p<0.0001).
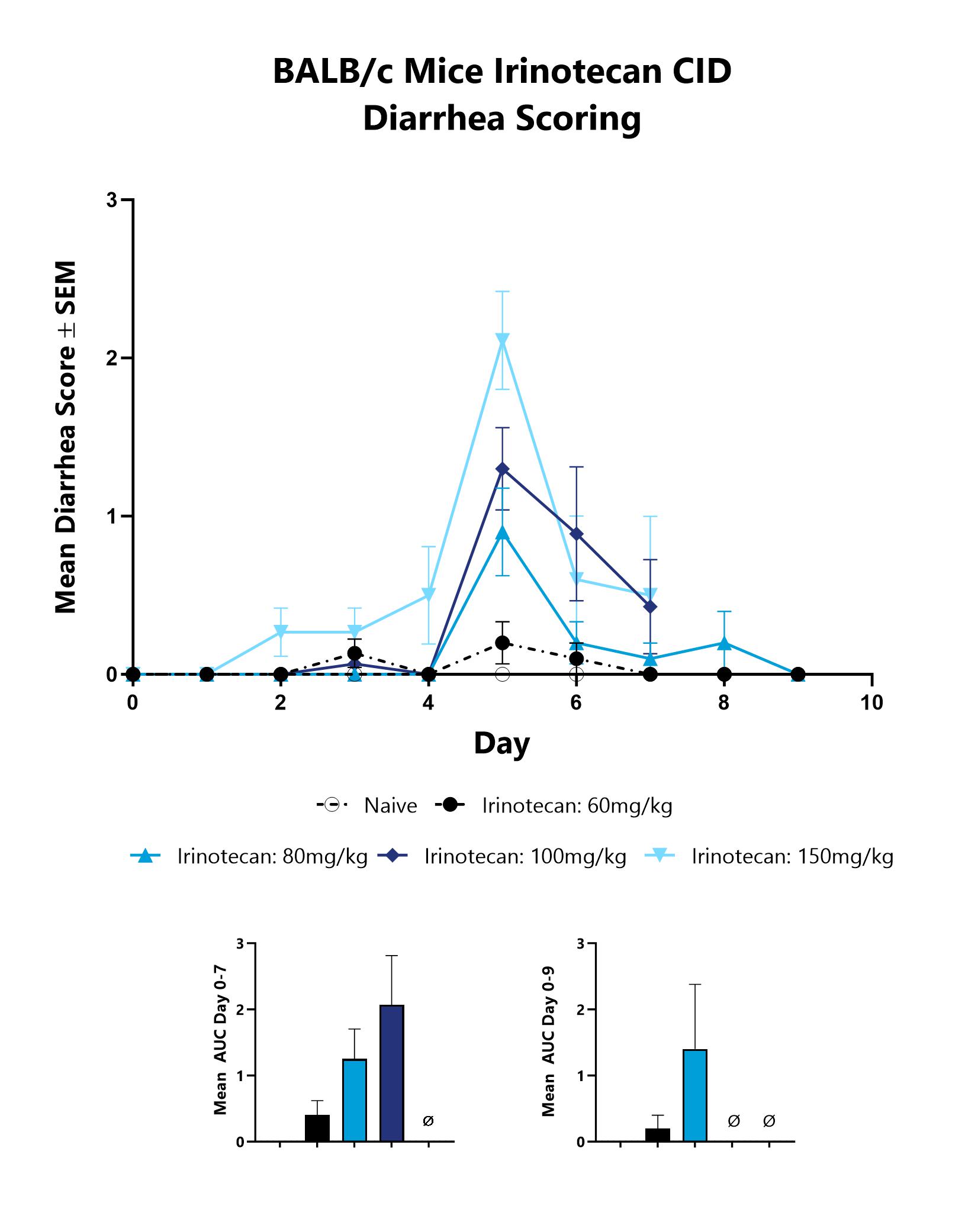
Mice with CID are assessed daily for diarrhea development. Each animal is assigned a score on a scale of 0-4, and the group mean is shown. The AUC is calculated to compare treatment arms and is shown in the inset.
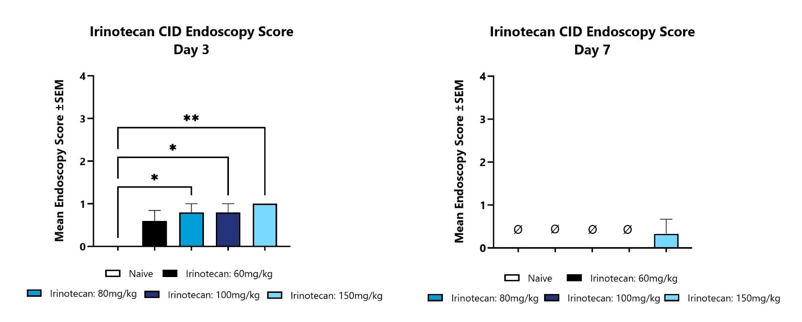
Animals with CID are assessed for colon inflammation by video endoscopy and are scored on a validated scale of 0-4. The mean group score is shown for Day 3 (left) and Day 7 (Right). (*p<0.05; **p<0.01; compared to the Naïve control group).

Close

At BioModels, you can assess your novel therapeutics for efficacy and mechanism of action in our established model of myelosuppression to address an unmet clinical need for patients. Cytotoxic chemotherapy drugs can lower cell levels in the bone marrow, resulting in abnormally low number of cells in the blood leading to symptoms that may result in reduction or breaks in cancer treatments. Myelosuppression is induced in mice or rats with one or two cycles of Doxorubicin. Animals are assessed daily over the course of the study for survival and weight change. Other important readouts include complete blood counts and bone marrow histology.
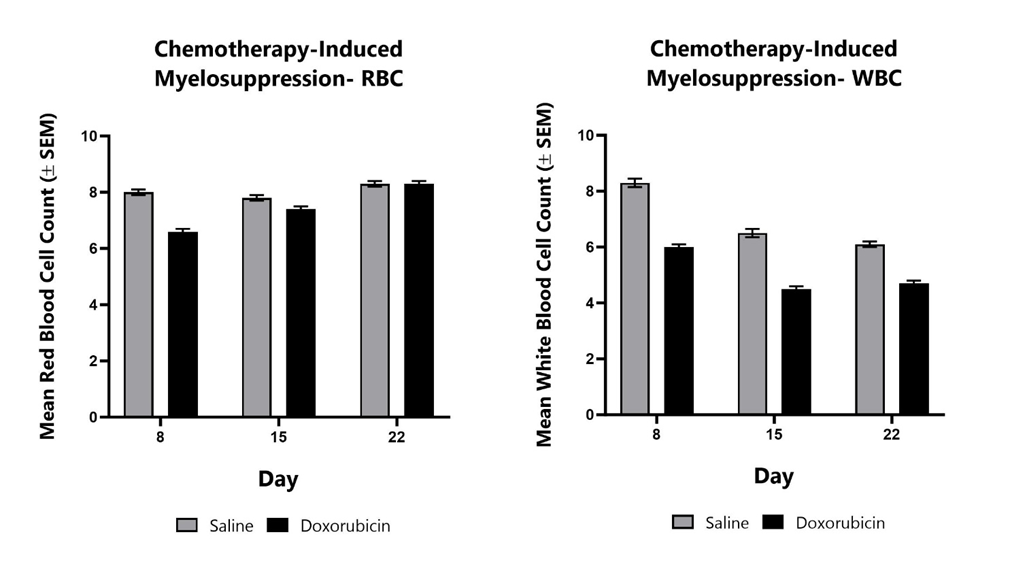
Animals treated with Doxorubicin from Day 1 to Day 3 are monitored for myelosuppression at various timepoints during the study by assessing the complete blood count. Mean red blood cell counts (left) and mean white blood cell counts (right) are shown compared to saline control animals.

Close

At BioModels, assess your novel therapeutic for efficacy and/or mechanism of action in our established model of cachexia/muscle wasting to address an unmet clinical need for patients. Cachexia, or wasting syndrome, is a complex, multifactorial metabolic disorder characterized by loss of appetite, fatigue, weight loss, and muscle mass loss. Disease is induced in mice through daily consumption of dexamethasone in the drinking water, as adverse side effects of high dose, continued usage of glucocorticoids has been demonstrated. Animals are assessed daily for body weight change and water consumption. Body composition analysis (DEXA) is evaluated at multiple timepoints during the study. At the conclusion of the study, select muscles are weighed for comparison between treatment groups.
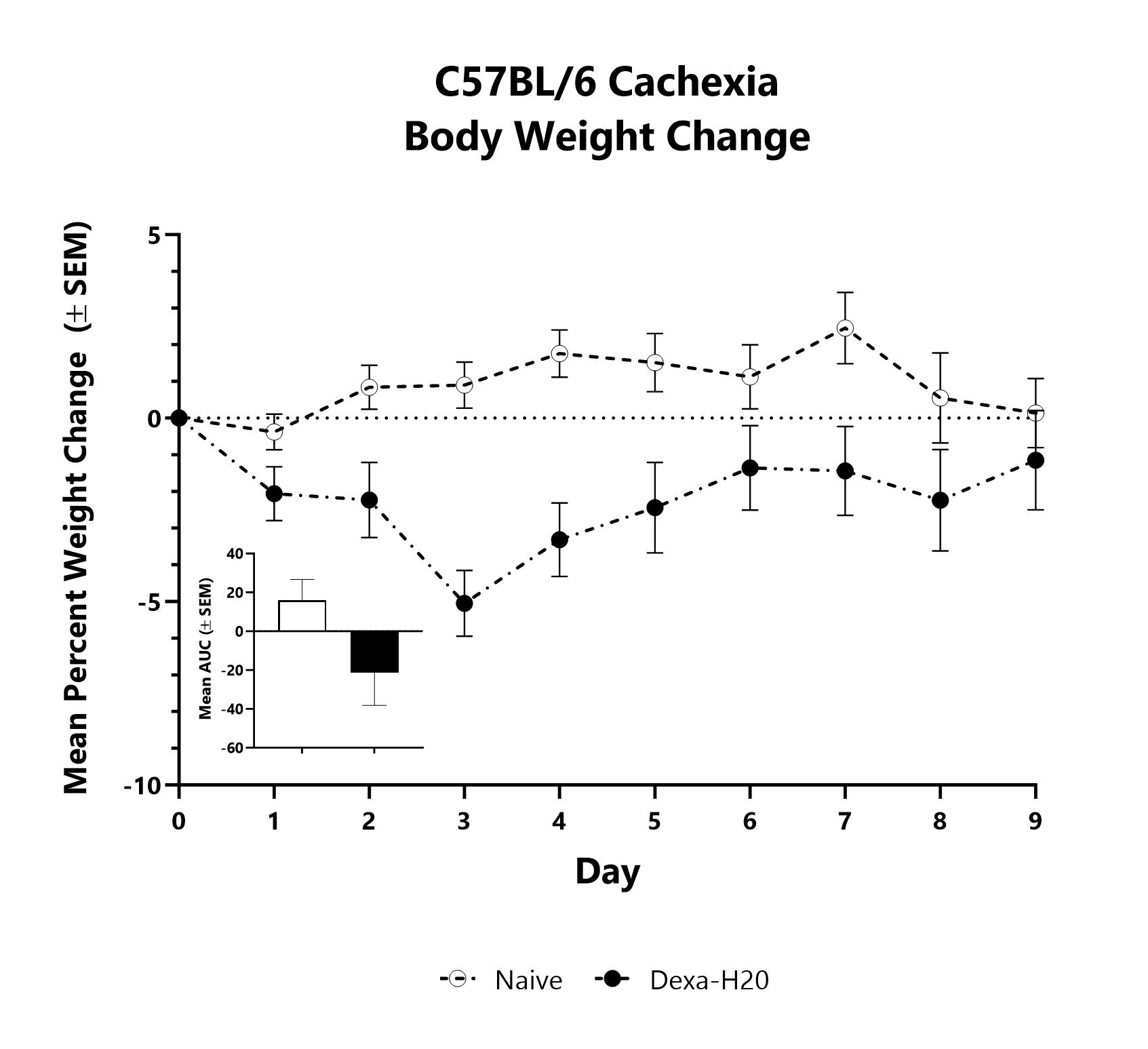
Dexamethasone is administered in the drinking water from Day 0 to Day 14 to induce muscle wasting. Animals are weighed daily, and body weight changes as compared to Day 0 are calculated. The AUC is calculated to compare treatment arms and is shown in the inset.
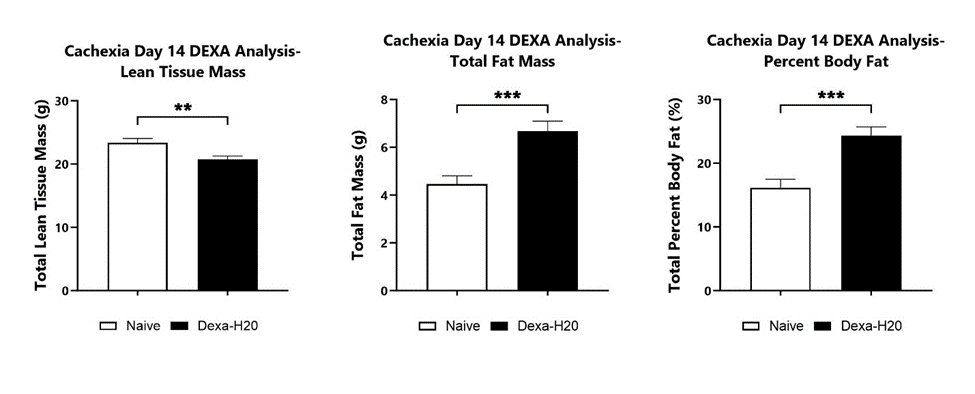
Dexamethasone is administered in the drinking water from Day 0 to Day 14 to induce muscle wasting. Body composition analysis is performed at various timepoints during the study. Day 14 DEXA analysis is shown including total lean tissue mass (left), total fat mass (middle), and total percent body fat (right). (**p<0.01; ***p<0.001).
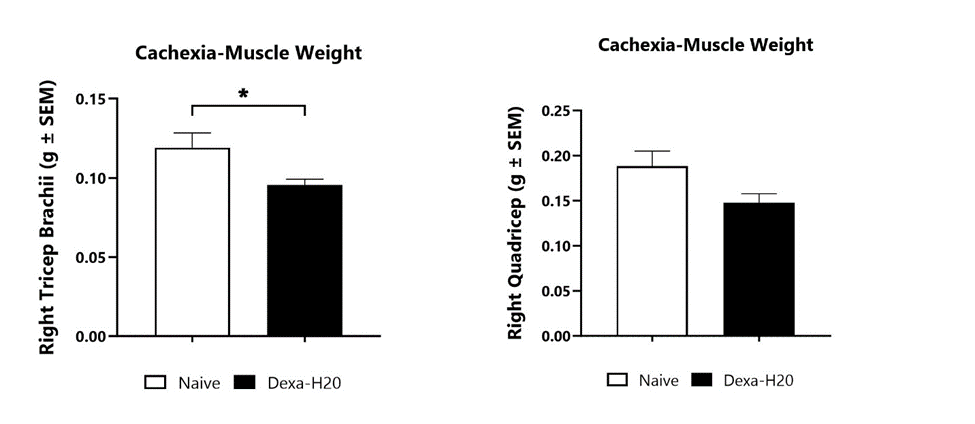
Dexamethasone is administered in the drinking water from Day 0 to Day 14 to induce muscle wasting. Muscle weights are determined at the study termination for various muscle groups. (*p<0.05).

Close