- Research Services
- Capabilities
- About Us
- Resources
- Contact Us
 Temperature Monitoring
Temperature Monitoring IVIS
IVIS DEXA
DEXA HD Endoscopy
HD Endoscopy Laser Doppler Blood Flow Monitor
Laser Doppler Blood Flow Monitor Tail Cuff Blood Pressure Monitor
Tail Cuff Blood Pressure Monitor Behavioral Assessment
Behavioral Assessment Metabolic Endpoints
Metabolic Endpoints Grip Strength Meter
Grip Strength Meter Administration Routes
Administration Routes In-Life Monitoring and Administration Routes
In-Life Monitoring and Administration RoutesThe ability to monitor and collect data from experimental animals during the course of a study is a key factor in a successful pre-clinical program. BioModels offers a variety of in-life monitoring options such as body temperature evaluation, IVIS, body composition analysis (DEXA), HD video endoscopy, and more allowing for longitudinal assessment of study subjects over time. BioModels also possesses expertise in multiple administration routes to support specific test material and disease model requirements.
BioModels offers a fully equipped facility to support:
Support your preclinical program with BioModels’ temperature monitoring capabilities. Body temperature can be a useful anaphylaxis readout in food allergy modeling experiments and can also be used to assess temperature changes following vaccination or test-article administration. We offer the ability to measure temperature of animals using subcutaneously implanted transponders that are read using a handheld wand.
Optical imaging can provide essential information for a variety of pre-clinical experiments, including oncology modeling studies, biodistribution studies, and more. In vivo imaging can be a critical tool for many preclinical oncology models, providing non-invasive, quantitative data on tumor pathology and tumor growth kinetics. Additionally, both in vivo and ex vivo imaging allows for visual assessment and quantification of the biodistribution of tagged compounds of interest for pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies. BioModels has 2D imaging capabilities for the detection of either bioluminescent or fluorescent compounds. Customizable study designs allow for flexible imaging timepoints to most accurately assess your marker of interest.
Support your preclinical program with BioModels’ DEXA imaging capabilities for body composition assessment. The dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) system enables a non-invasive approach for bone and body tissue analysis in mouse models. DEXA evaluations can be performed at various timepoints throughout the study, providing important information about body composition over time and the response of these phenotypes to test treatments.
Endoscopic evaluation is critical for determining the efficacy of experimental compounds in the treatment of IBD and colitis. The use of video endoscopy for IBD and colitis rodent models provides a method for daily visual assessment of colitis severity as well as tracking of mucosal healing following a therapeutic intervention. Our skilled technicians carefully perform endoscopic evaluation to monitor disease progression using a five-point scale to generate a colitis score. Endoscopic evaluations can be performed at various time points throughout a study, providing important information about disease progression over time and the response of disease to test treatments.
The Laser Doppler Blood Flow monitor provides critical information in a wide range of research applications where blood supply has been disrupted. The Laser Doppler Blood Flow monitor enables measurement of microvascular blood perfusion in disease models including venous thrombosis and pulmonary disease. BioModels’ has options for non-invasive surface probes that can be applied to the skin of the animal or for more invasive and refined measures, a needle probe can be applied directly to exposed muscle or to a vein or artery of interest.
The tail cuff blood pressure monitor is a useful tool for in-life monitoring in rodent models. The tail cuff blood pressure monitor enables non-invasive longitudinal measures of systolic and diastolic blood pressure in disease models such as hypertension. BioModels’ has options for high throughput monitoring of animals.
Support your preclinical program with BioModels’ behavioral assessment capabilities. We offer capabilities for testing depression, anxiety, pain, neuropathy, motor dysfunction, and more.
Support your preclinical program with BioModels’ comprehensive metabolic endpoint capabilities. We offer established and custom approaches to characterize metabolic disease phenotypes, whether in support of validated animal models or as standalone experiments. Analysis of samples generated in your lab or by collaborators is also available.
Support your preclinical program with BioModels’ grip strength measuring capabilities. We offer the ability to measure grip strength of fore and hind limbs in mice and rats as a longitudinal measure. Grip strength assessment can be a useful readout for any model where muscle weakness is an anticipated phenotype, including Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis and more.
Support your preclinical program with BioModels’ dosing route capabilities. We offer numerous routes of administration for test articles and disease induction. If the route you are interested in is not listed below, we’d be happy to discuss further as our highly experienced animal technicians can quickly learn a new technique.
Capabilities


Close
Capabilities

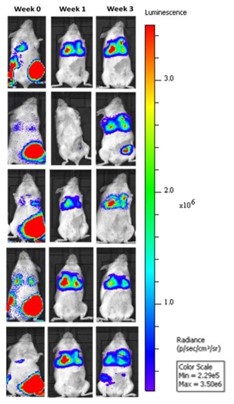
Patient derived triple-negative breast cancer tumors expressing a bioluminescent reporter (HBCx-14-Luc) are seeded into the fourth mammary fat pad in immunocompromised mice and then resected after growth criteria is met. Upon resection of the primary tumors (Week 0), treatment paradigms are introduced, and metastatic progression is monitored in the lungs of the animals via IVIS imaging to detect luminescence.

Close
Capabilities

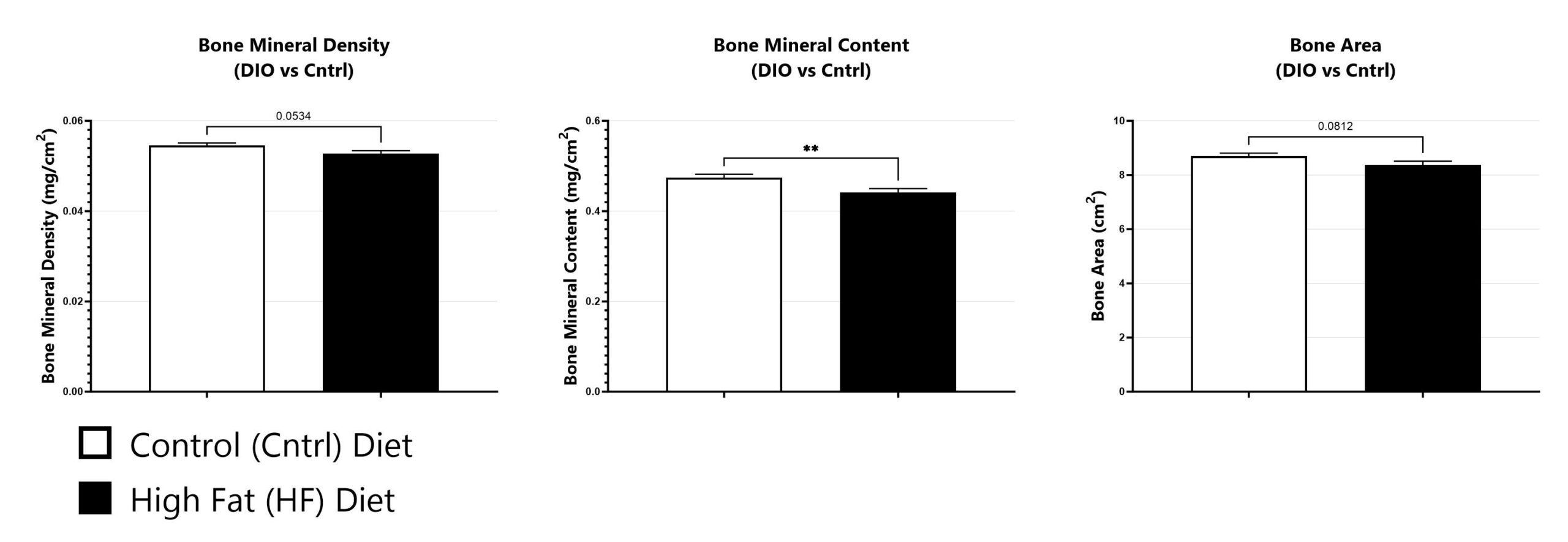
Animals are assessed for bone mineral density, bone mineral content, and bone area by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) six weeks following introduction of high-fat or control diets. (**p<0.01).
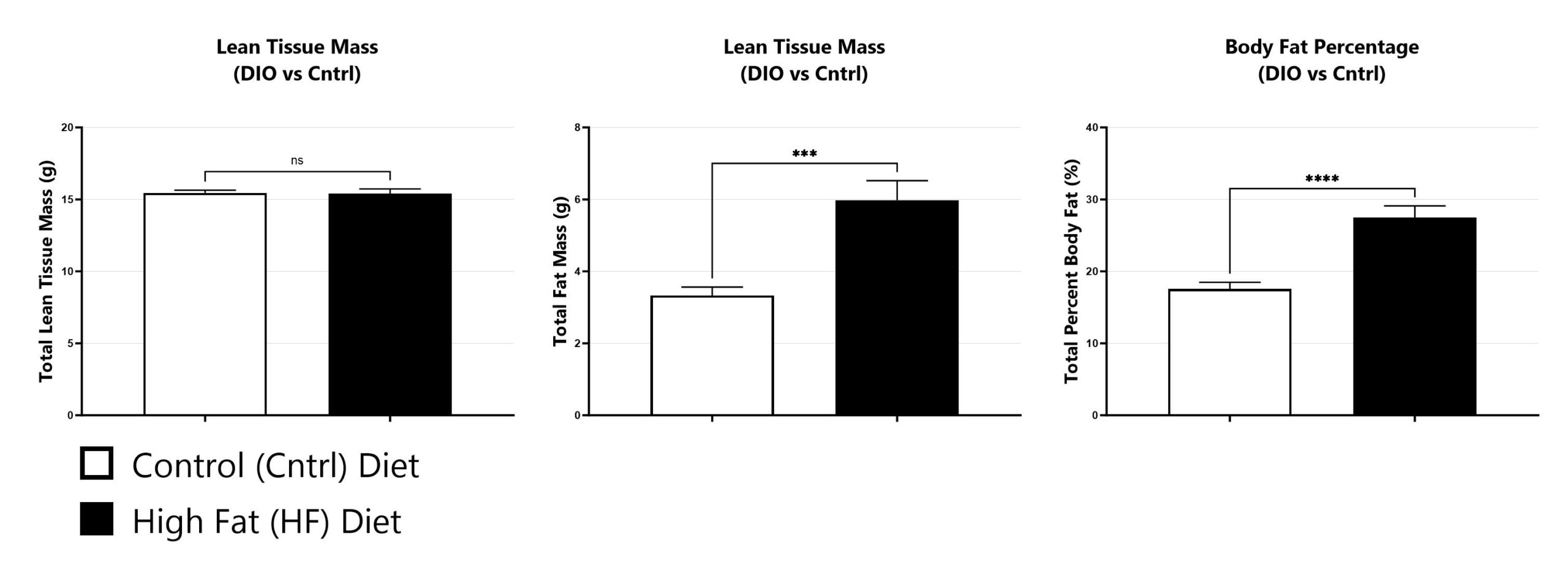
Animals are assessed for lean tissue mass, fat mass, and body fat percentage by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) six weeks following introduction of high-fat or control diets. (***p<0.005; ****p<0.001).

Close
Capabilities

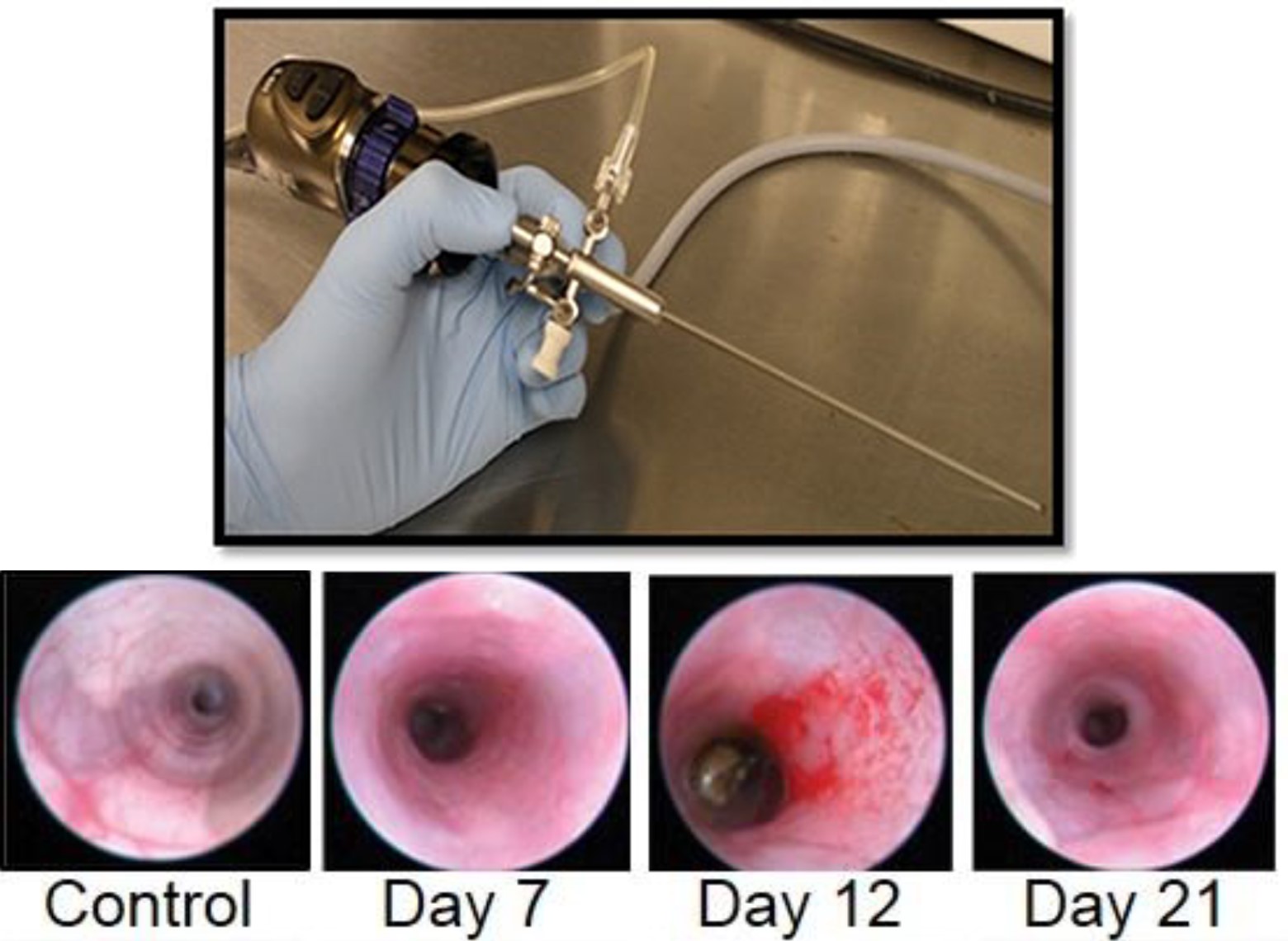
DSS-induced animals are assessed for colonic inflammation and ulceration by video endoscopy and are scored for colitis severity on multiple days.

Close
Capabilities
Capabilities

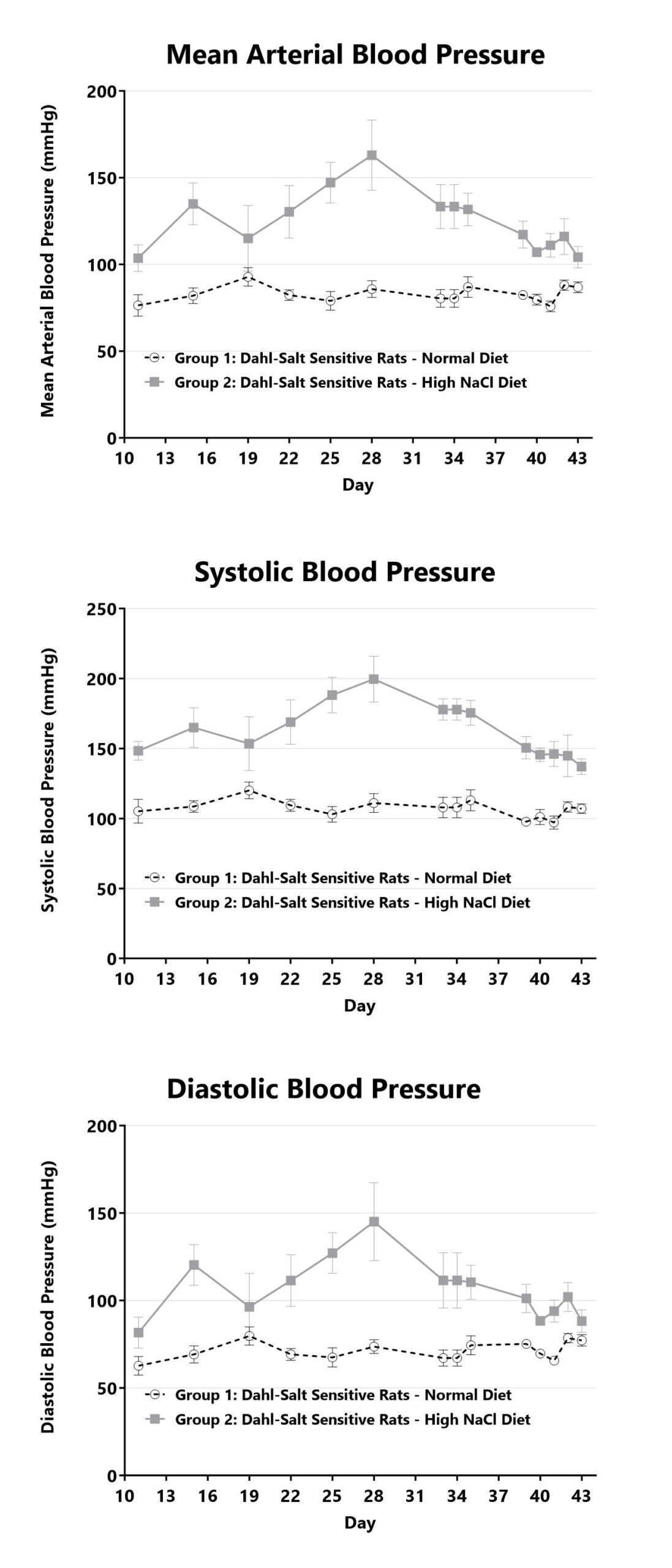
Blood pressure is monitored twice a week in Dahl-Salt sensitive rats using a non-invasive blood pressure system to measure mean arterial blood pressure (top), systolic blood pressure (middle) and diastolic blood pressure (bottom).

Close
Capabilities

Assess motor coordination, motor learning, and physical condition by RotaRod test. Animals are placed on an elevated, horizontally oriented dowel. The dowel rotates at a predetermined speed, acceleration, and maximum duration, or until the animal falls from the dowel. Latency to fall for each animal is measured on every trial. Performance may be measured over the course of multiple days, with repeated trials per day.
Assess anxiety-like behavior and motor activity with the open field test. The open field test is among the most widely used procedures in behavioral testing. Motor function is measured by evaluating spontaneous activity in the open field, whereas anxiety is measured by evaluating time spent in the open field. Rodents have a natural aversion to open spaces and tend to prefer the areas close to the walls of the apparatus. Anxiolytic compounds will increase time spent in the middle of the open field.
Assess disease induction or test-article effects on activity and circadian rhythm in BioModels’ running wheel behavior suite. Our suite has over 100 available running wheels and enables detailed activity readouts 24 hours per day, with altered light/dark schedules available.
Assess disease induction or test-article effects on memory with the Object Recognition Test. The Object Recognition Test capitalizes on rodents’ natural affinity toward novel objects when in a novel environment. Activity is monitored using video cameras interfaced with video tracking software. Time spent investigating the objects is measured.
Determine disease induction or test-article effects on sociability with the Social Approach test. Deficits in social functioning are a feature of many diseases including depression, agoraphobia, and autism. Time spent with conspecific object vs inanimate object will be automatically measured using video tracking software.
Assess disease induction or test article effects on learning and memory with the Fear Conditioning Test. The test examines the animals’ behavioral response when placed in a previously aversive environment in order to determine if the animal remembers the environment. Animals that demonstrate the instinctual fear response of freezing are inferred to have recognized the environment, thus remembering their previous experience. Locomotor activity and freezing behavior are automatically recorded using video tracking software.
Utilize forced exercise on a rodent treadmill to assess test article effects in the mdx mouse model of muscular dystrophy, induce stress response, or assess responses to exercise that voluntary activity (wheel running) are unable to invoke.
Determine disease induction or test article effects on anxiety-behavior with the Elevated Plus Maze Test. An animal’s preference for being in open arms vs closed arms is calculated to determine anxiety-like behavior. Activity is recorded with video tracking software.
Assess disease induction or test article effects on restricted repetitive behaviors with the Repetitive Grooming Test. Though most often associated with autism in humans, restricted repetitive behaviors are also observed in other disorders such as Rett, Fragile X, and Prader-Willi syndromes; in mice, this phenotype may present as repetitive grooming. Individual animals’ grooming behavior is automatically recorded using video tracking software.
Assess disease induction or test article effects on circadian rhythm and other behaviors by altering light/dark cycle. Following habituation to the 12:12 hr light/dark cycle, the light cycle can be shifted by up to 12 hours. This results in alteration of the active or sleep periods. The new light/dark cycle is maintained for a minimum of seven days. Multiple phase shifts can be applied over the course of a study to explore more complex scientific questions.
Assess disease induction or test article effects on depression phenotypes with the Forced Swim Test. The test is a routinely used assay for the study of depressive-like behavior in rodents. It is based on the assumption that, when placed in a container of water, mice will at first attempt to escape but will eventually exhibit immobility, which may reflect behavioral despair. The test is automatically recorded using video tracking software and time until immobility is observed is determined.
Assess disease induction or test article effects on depression phenotypes with the Tail Suspension Test. Similar to the Forced Swim Test, the Tail Suspension Test measures behavioral despair and learned helplessness. When suspended by their tail, animals will at first attempt to escape but will eventually become immobile. The test is automatically recorded using video tracking software and time until immobility is observed is determined.
Support your preclinical program with BioModels’ grip strength measuring capabilities. We offer the ability to measure grip strength of fore and hind limbs in mice and rats as a longitudinal measure. Grip strength assessment can be a useful readout for any model where muscle weakness is an anticipated phenotype, including Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis and more.

Close
Capabilities

As alterations in feeding can be a part of metabolic disorders, quantifying food and water as well as urine and feces can be performed longitudinally to measure energy and fluid homeostasis. Standard or custom study design options support experiments unique to your program and hypothesis.

Close

Measuring glucose and insulin sensitivity is a widely published tool, with utility across the drug discovery pipeline. BioModels offers standard and custom experimental design options for assessing metabolic profiles. Custom study design options support experiments unique to your program and hypothesis.

Close

Blood glucose monitoring allows for longitudinal assessment of the metabolic state of animals throughout a study. Using a single drop of blood, quantitative glucose levels can be assessed in animals. Analyze blood samples generated at BioModels in one of our preclinical animal models.

Close

Blood chemistry analysis allows for longitudinal assessment of multiple systemic markers of disease in a single sample. Using a small 100 µL serum or plasma sample, quantitative values are reported for the specified readouts providing a snapshot of the animal’s health or a downstream effect of an experimental treatment. Analyze blood samples generated at BioModels in one of our preclinical animal models, or assess samples generated in your lab or by a collaborator.
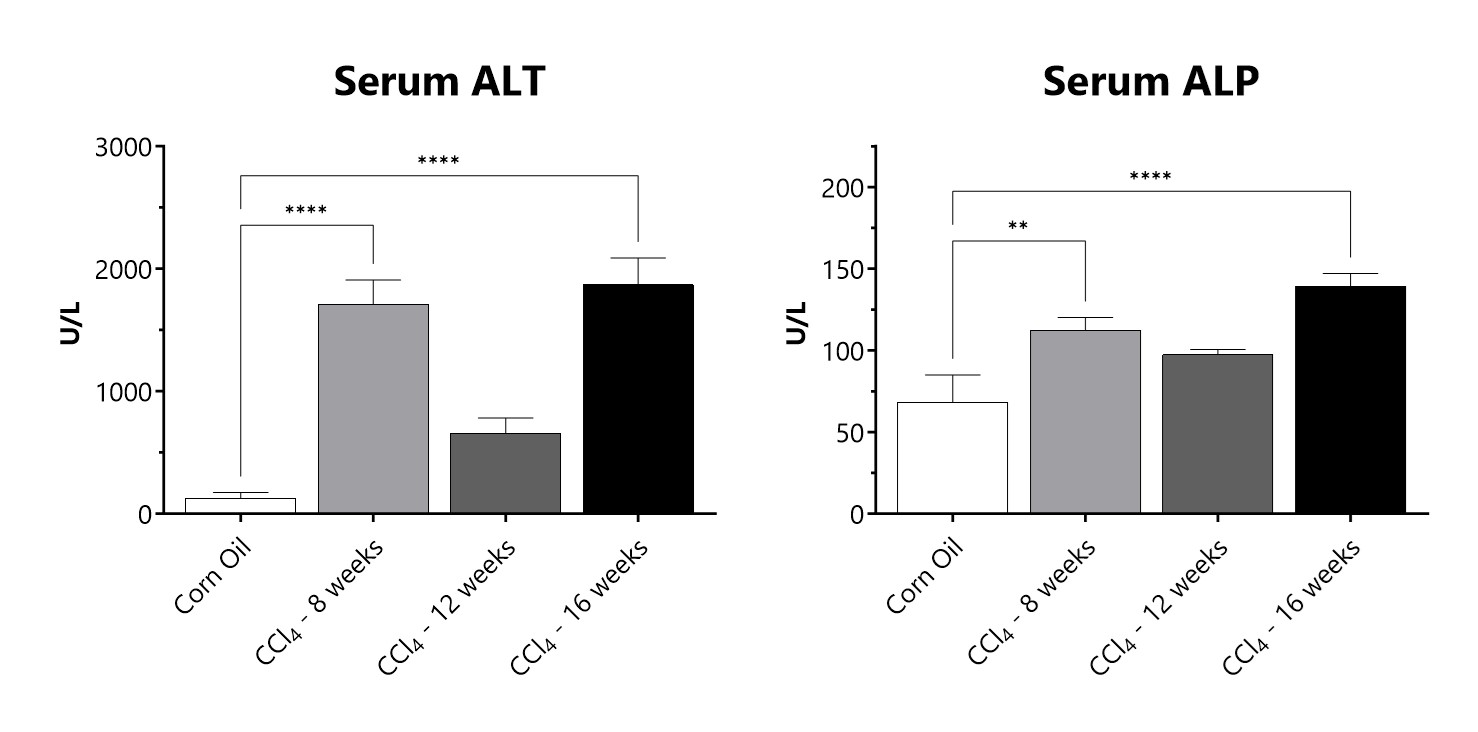
Serum samples from CCl4 administered animals are assessed for levels of alanine transaminase (ALT) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP). (**p<0.01; ****p<0.0001 compared to the corn oil control group)

Close